Kinetic energy remains constant in uniform circular motion, as explained by onlineuniforms.net. This is because the speed of the object stays constant, and no work is done on the object. Discover stylish and durable uniform solutions at onlineuniforms.net, and explore various work apparel and professional clothing options to enhance your team’s appearance.
1. What is Uniform Circular Motion and How Does It Relate to Kinetic Energy?
Uniform circular motion is the movement of an object at a constant speed along a circular path. The kinetic energy of an object is the energy it possesses due to its motion. Therefore, kinetic energy depends on both mass and velocity.
1.1 Defining Uniform Circular Motion
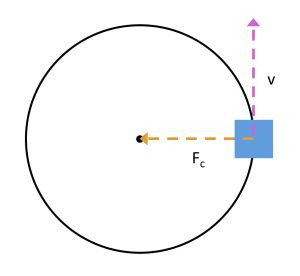
Uniform circular motion occurs when an object moves in a circle at a constant speed. Although the speed is constant, the velocity is not, because the direction of motion is always changing. This change in direction means the object is constantly accelerating towards the center of the circle. This acceleration is known as centripetal acceleration and is caused by a centripetal force, which is always directed towards the center of the circle.
1.2 The Formula for Kinetic Energy
Kinetic energy (KE) is calculated using the following formula:
KE = 1/2 * mv^2
Where:
- m = mass of the object
- v = speed of the object
This formula shows that kinetic energy is directly proportional to the square of the speed. If the speed remains constant, as it does in uniform circular motion, then the kinetic energy also remains constant, provided the mass does not change.
1.3 Examples of Uniform Circular Motion
Here are some common examples of uniform circular motion:
- A satellite orbiting the Earth at a constant speed: The satellite’s speed remains constant, and it follows a circular path around the Earth.
- A car moving around a circular track at a constant speed: As long as the car maintains a constant speed, it is in uniform circular motion.
- The tip of a fan blade rotating at a constant speed: Each point on the fan blade moves in a circle at a constant speed.
2. Why is Kinetic Energy Constant in Uniform Circular Motion?
Kinetic energy is constant in uniform circular motion because the speed of the object remains constant. Since kinetic energy depends only on speed and mass, and neither of these changes, the kinetic energy remains constant.
2.1 Constant Speed in Uniform Circular Motion
In uniform circular motion, the object’s speed is constant. This means that the magnitude of the velocity vector does not change. Although the direction of the velocity vector is constantly changing, only the magnitude affects the kinetic energy.
2.2 No Change in Mass
The mass of the object in motion remains constant. Unless there is a change in mass, such as through the addition or subtraction of material, the mass term in the kinetic energy equation remains constant.
2.3 The Role of Centripetal Force
Centripetal force is crucial for maintaining uniform circular motion, but it does not change the object’s kinetic energy. The centripetal force is always directed towards the center of the circle, perpendicular to the object’s direction of motion. Because the force is perpendicular to the displacement, no work is done on the object.
3. What is Work and How Does It Relate to Kinetic Energy?
Work is defined as the force applied to move an object over a certain displacement. The work-energy theorem states that the work done on an object is equal to the change in its kinetic energy.
3.1 Definition of Work
Work (W) is calculated using the following formula:
W = F d cos(θ)
Where:
- F = magnitude of the force
- d = magnitude of the displacement
- θ = angle between the force and displacement vectors
Only the component of the force in the direction of motion contributes to the work being done.
3.2 The Work-Energy Theorem
The work-energy theorem states that the net work done on an object is equal to the change in its kinetic energy:
W = ΔKE = KE_final – KE_initial
If the net work done on an object is zero, then there is no change in its kinetic energy, and the kinetic energy remains constant.
3.3 No Work is Done in Uniform Circular Motion
In uniform circular motion, the centripetal force is always perpendicular to the direction of motion. This means that the angle θ between the force and displacement vectors is 90 degrees. Since cos(90°) = 0, the work done by the centripetal force is zero:
W = F d cos(90°) = 0
Therefore, no work is done on the object in uniform circular motion, and its kinetic energy remains constant.
4. Mathematical Proof That Kinetic Energy is Constant
To mathematically prove that kinetic energy is constant in uniform circular motion, we can use the definitions of work, kinetic energy, and the properties of circular motion.
4.1 Defining Velocity in Uniform Circular Motion
In uniform circular motion, the velocity vector v can be expressed as:
v = v(cos(θ)i + sin(θ)j)
Where:
- v = constant speed
- θ = angle that changes with time (θ = ωt, where ω is the angular velocity)
- i and j = unit vectors in the x and y directions
4.2 Defining Force in Uniform Circular Motion
The centripetal force F can be expressed as:
F = -F(cos(θ)i + sin(θ)j)
Where F is the magnitude of the centripetal force. The negative sign indicates that the force is directed towards the center of the circle.
4.3 Calculating Work Done
The work done can be expressed as the dot product of force and displacement:
W = ∫ F ⋅ ds
Where ds is an infinitesimal displacement vector. Since F is always perpendicular to ds in uniform circular motion, their dot product is zero:
F ⋅ ds = 0
Therefore, the work done is zero:
W = ∫ 0 dt = 0
4.4 Applying the Work-Energy Theorem
According to the work-energy theorem:
ΔKE = W
Since W = 0:
ΔKE = 0
This means that the change in kinetic energy is zero, and the kinetic energy remains constant.
5. Common Misconceptions About Kinetic Energy and Circular Motion
Several misconceptions exist regarding kinetic energy and circular motion. Clarifying these can help to solidify understanding.
5.1 Misconception: Constant Velocity Implies Constant Kinetic Energy in All Situations
Constant velocity implies constant kinetic energy only when the mass also remains constant. If an object’s mass changes while its velocity is constant, its kinetic energy will also change.
5.2 Misconception: Centripetal Force Does Work Because It Causes Acceleration
Centripetal force causes acceleration by changing the direction of the velocity, but it does not do work because it is always perpendicular to the displacement. Work requires a component of force in the direction of displacement.
5.3 Misconception: Kinetic Energy Changes Because the Direction of Motion Changes
Kinetic energy depends only on the magnitude of the velocity (speed), not its direction. Therefore, changes in the direction of motion do not affect kinetic energy as long as the speed remains constant.
6. Real-World Applications of Uniform Circular Motion
Understanding uniform circular motion and its implications for kinetic energy is essential in various real-world applications.
6.1 Satellites in Orbit
Satellites orbiting the Earth at a constant speed experience uniform circular motion. Their kinetic energy remains constant as long as their speed and mass do not change. This is crucial for maintaining stable orbits.
6.2 Rotational Machines
Many machines involve rotating parts that undergo uniform circular motion. For example, the rotor in an electric motor or the blades of a turbine maintain constant kinetic energy as they rotate at a constant speed.
6.3 Amusement Park Rides
Several amusement park rides, such as Ferris wheels and rotating swings, are designed based on the principles of uniform circular motion. The kinetic energy of the riders remains constant as they move in a circle at a constant speed, providing a thrilling yet safe experience.
7. How to Calculate Kinetic Energy in Uniform Circular Motion
Calculating kinetic energy in uniform circular motion is straightforward as long as you know the object’s mass and speed.
7.1 Steps to Calculate Kinetic Energy
- Determine the Mass (m): Find the mass of the object in kilograms (kg).
- Determine the Speed (v): Find the speed of the object in meters per second (m/s).
- Apply the Formula: Use the formula KE = 1/2 * mv^2 to calculate the kinetic energy.
- State the Units: The kinetic energy will be in joules (J).
7.2 Example Calculation
Suppose a satellite with a mass of 500 kg is orbiting the Earth at a constant speed of 7,000 m/s. To calculate its kinetic energy:
KE = 1/2 (500 kg) (7,000 m/s)^2
KE = 1/2 500 49,000,000
KE = 12,250,000,000 J
Therefore, the kinetic energy of the satellite is 12.25 billion joules.
7.3 Factors Affecting Kinetic Energy Calculation
- Accuracy of Measurements: Accurate measurements of mass and speed are essential for precise kinetic energy calculations.
- Constant Speed: Ensure the speed is truly constant, as any variations will affect the kinetic energy.
- Units: Use consistent units (kg for mass and m/s for speed) to obtain the kinetic energy in joules.
8. The Relationship Between Angular Velocity and Kinetic Energy
While kinetic energy is directly related to linear speed, it is also connected to angular velocity in circular motion.
8.1 Defining Angular Velocity
Angular velocity (ω) is the rate at which an object rotates or revolves relative to a point, i.e. how fast an object changes its angle. It is measured in radians per second (rad/s).
8.2 The Relationship Between Linear and Angular Velocity
The linear speed (v) of an object in uniform circular motion is related to its angular velocity (ω) by the following equation:
v = rω
Where r is the radius of the circular path.
8.3 Kinetic Energy in Terms of Angular Velocity
Substituting v = rω into the kinetic energy formula, we get:
KE = 1/2 * m(rω)^2
KE = 1/2 * mr^2ω^2
Since the moment of inertia (I) for a point mass is I = mr^2, the kinetic energy can also be expressed as:
KE = 1/2 * Iω^2
This shows that kinetic energy is proportional to the square of the angular velocity. If the angular velocity is constant, the kinetic energy remains constant.
9. Impact of External Forces on Kinetic Energy in Circular Motion
While ideal uniform circular motion assumes no external forces affecting the object’s speed, real-world scenarios often involve external influences.
9.1 Friction and Air Resistance
Friction and air resistance are common external forces that can affect the kinetic energy of an object in circular motion. These forces oppose the motion and do negative work, reducing the object’s speed and kinetic energy.
9.2 Applied Forces
If an external force is applied in the direction of motion, it will do positive work and increase the object’s speed and kinetic energy. Conversely, if an external force is applied opposite to the direction of motion, it will do negative work and decrease the object’s speed and kinetic energy.
9.3 Maintaining Constant Kinetic Energy
To maintain constant kinetic energy in the presence of external forces, a compensating force must be applied to counteract the effects of these forces. For example, in a car moving around a circular track, the engine must provide enough force to overcome friction and air resistance, keeping the speed constant.
10. Advanced Concepts: Non-Uniform Circular Motion
Non-uniform circular motion occurs when the speed of the object changes as it moves along the circular path. In this case, the kinetic energy is not constant.
10.1 Definition of Non-Uniform Circular Motion
Non-uniform circular motion involves both centripetal acceleration (due to the change in direction) and tangential acceleration (due to the change in speed). The net force is no longer directed towards the center of the circle but has a tangential component.
10.2 Changing Kinetic Energy
In non-uniform circular motion, the speed of the object changes, and therefore, its kinetic energy also changes. The work-energy theorem applies, and the change in kinetic energy is equal to the net work done on the object.
10.3 Examples of Non-Uniform Circular Motion
- A roller coaster going through a loop: The roller coaster’s speed changes as it moves around the loop, with the highest speed at the bottom and the lowest speed at the top.
- A car accelerating around a circular track: If the car’s driver accelerates, the car’s speed increases, and it undergoes non-uniform circular motion.
- A spinning top slowing down due to friction: As the spinning top loses energy due to friction, its angular speed decreases, and it undergoes non-uniform circular motion.
11. Practical Examples of Uniform Circular Motion in Everyday Life
Uniform circular motion isn’t just a theoretical concept; it’s present in many aspects of daily life.
11.1 CD and DVD Players
In CD and DVD players, the disc rotates at a constant speed, allowing the laser to read the data accurately. This is an example of uniform circular motion, where the kinetic energy of the disc remains constant during playback.
11.2 Washing Machines
Washing machines use uniform circular motion during the spin cycle to remove water from clothes. The drum rotates at a high, constant speed, and the kinetic energy of the clothes remains constant as they move in a circle.
11.3 Ceiling Fans
Ceiling fans provide a refreshing breeze by using uniform circular motion. The blades rotate at a constant speed, and the kinetic energy of each point on the blade remains constant, ensuring a steady airflow.
12. Advanced Physics Concepts Related to Circular Motion
Circular motion is a fundamental concept in physics with links to more advanced topics.
12.1 Conservation of Angular Momentum
In a closed system, the total angular momentum remains constant if no external torque acts on it. This principle is closely related to uniform circular motion and explains phenomena like the spinning of ice skaters pulling their arms in to increase their rotation speed.
12.2 Coriolis Effect
The Coriolis effect is an apparent deflection of moving objects when viewed from a rotating reference frame. It affects weather patterns, ocean currents, and even the trajectory of long-range projectiles.
12.3 General Relativity
Einstein’s theory of general relativity describes gravity as the curvature of spacetime caused by mass and energy. Objects in orbit around a massive body follow curved paths in spacetime, which can be analyzed using principles of circular motion.
13. The Significance of Understanding Kinetic Energy in Uniform Circular Motion
Understanding kinetic energy in uniform circular motion is not only crucial for physics students but also has practical implications for engineers, designers, and anyone working with rotating systems.
13.1 Engineering Applications
Engineers use the principles of uniform circular motion and kinetic energy to design and analyze rotating machinery, such as turbines, motors, and gears. They must ensure that these systems operate efficiently and safely, maintaining constant kinetic energy and minimizing energy losses.
13.2 Safety Considerations
Understanding kinetic energy in circular motion is essential for ensuring the safety of amusement park rides, vehicles, and other systems involving rotating parts. Designers must account for the forces and energies involved to prevent accidents and injuries.
13.3 Optimizing Performance
By understanding the factors that affect kinetic energy in circular motion, designers can optimize the performance of rotating systems. For example, they can reduce friction and air resistance to minimize energy losses and increase efficiency.
14. Key Takeaways: Is Kinetic Energy Constant in Uniform Circular Motion?
Reiterating the main points helps reinforce understanding.
14.1 Uniform Circular Motion Defined
Uniform circular motion is the movement of an object at a constant speed along a circular path. Although the speed is constant, the velocity is not, because the direction of motion is always changing.
14.2 Constant Kinetic Energy
In uniform circular motion, the kinetic energy of the object remains constant because its speed and mass do not change. The centripetal force, which is always perpendicular to the direction of motion, does no work on the object.
14.3 The Work-Energy Theorem
The work-energy theorem states that the net work done on an object is equal to the change in its kinetic energy. Since no work is done in uniform circular motion, the kinetic energy remains constant.
15. Find the Perfect Uniforms at Onlineuniforms.net
Looking for high-quality and stylish uniforms for your business, school, or organization? Visit onlineuniforms.net to explore our wide selection of work apparel, professional clothing, and custom uniform options. Ensure your team looks professional and feels comfortable with our durable and affordable uniform solutions.
15.1 Wide Range of Uniform Options
At onlineuniforms.net, we offer a diverse range of uniform options to suit various industries and professions. Whether you need medical scrubs, chef uniforms, school uniforms, or corporate attire, we have you covered.
15.2 Customization Services
Make your uniforms unique with our customization services. Add your company logo, employee names, or custom designs to create a professional and branded look. Our customization options include embroidery, screen printing, and heat transfer.
15.3 High-Quality and Durable Materials
We use only the highest quality materials to ensure that our uniforms are durable, comfortable, and long-lasting. Our fabrics are designed to withstand the rigors of daily wear and tear, keeping your team looking sharp and professional.
16. Elevate Your Brand with Custom Uniforms from Onlineuniforms.net
Custom uniforms are a powerful tool for enhancing your brand identity and creating a cohesive team image. With onlineuniforms.net, you can easily design and order custom uniforms that reflect your brand values and style.
16.1 Create a Professional Image
Custom uniforms help create a professional and polished image for your business. When your employees wear branded uniforms, they project a sense of professionalism and credibility to your customers.
16.2 Enhance Brand Recognition
Custom uniforms with your company logo and colors help enhance brand recognition and visibility. When your employees wear branded uniforms in public, they act as walking billboards, promoting your brand to a wider audience.
16.3 Build Team Cohesion
Custom uniforms can help build team cohesion and a sense of belonging among your employees. When everyone wears the same uniform, it creates a sense of unity and camaraderie, fostering a positive work environment.
17. Uniform Solutions for Every Industry at Onlineuniforms.net
No matter what industry you’re in, onlineuniforms.net has the perfect uniform solutions for your needs. We offer a wide selection of uniforms for healthcare, hospitality, education, and corporate sectors.
17.1 Healthcare Uniforms
Our healthcare uniforms are designed for comfort, durability, and hygiene. We offer a variety of scrubs, lab coats, and medical apparel that meet the highest standards of quality and performance.
17.2 Hospitality Uniforms
Our hospitality uniforms are stylish, functional, and designed to make a lasting impression. We offer a range of chef coats, server aprons, and restaurant uniforms that reflect the unique atmosphere of your establishment.
17.3 Education Uniforms
Our education uniforms are comfortable, durable, and designed to promote a sense of unity and pride among students. We offer a variety of school uniforms, including shirts, pants, skirts, and jackets, in a range of sizes and colors.
18. The Importance of Properly Fitted Uniforms
The fit of a uniform can significantly impact an employee’s comfort, performance, and overall appearance. Properly fitted uniforms not only look better but also allow for greater mobility and ease of movement.
18.1 Comfort and Mobility
Uniforms that are too tight can restrict movement and cause discomfort, while those that are too loose can be cumbersome and unprofessional. Properly fitted uniforms allow employees to perform their duties comfortably and efficiently.
18.2 Professional Appearance
Well-fitted uniforms contribute to a polished and professional appearance. Employees who wear uniforms that fit well project confidence and competence, enhancing the company’s image.
18.3 Safety Considerations
In some industries, such as healthcare and construction, properly fitted uniforms are essential for safety. Uniforms that are too loose can get caught in machinery or equipment, while those that are too tight can restrict movement and impair performance.
19. Trends in Uniform Design and Materials
The uniform industry is constantly evolving, with new trends in design and materials emerging all the time. Staying up-to-date with these trends can help you choose uniforms that are both stylish and functional.
19.1 Sustainable Materials
Sustainable materials are becoming increasingly popular in the uniform industry. Fabrics made from recycled materials, organic cotton, and bamboo are eco-friendly and offer excellent comfort and durability.
19.2 Performance Fabrics
Performance fabrics are designed to wick away moisture, resist stains, and provide enhanced comfort. These fabrics are ideal for uniforms in industries where employees are active and need to stay cool and dry.
19.3 Modern Designs
Modern uniform designs are sleek, stylish, and functional. They often incorporate features such as hidden pockets, adjustable closures, and ergonomic cuts to enhance comfort and performance.
20. Innovations in Uniform Technology
Technology is playing an increasing role in the uniform industry, with innovations such as smart fabrics, wearable sensors, and enhanced safety features. These advancements are improving the functionality, comfort, and safety of uniforms.
20.1 Smart Fabrics
Smart fabrics are textiles that can sense and respond to environmental stimuli, such as temperature, pressure, and moisture. These fabrics can be used to create uniforms that regulate body temperature, monitor vital signs, and provide enhanced comfort.
20.2 Wearable Sensors
Wearable sensors can be integrated into uniforms to monitor employees’ health and safety. These sensors can track heart rate, body temperature, and activity levels, providing valuable data for employers and employees.
20.3 Enhanced Safety Features
Uniforms with enhanced safety features, such as reflective strips, flame-resistant materials, and cut-resistant fabrics, can help protect employees from hazards in the workplace. These features are essential for industries such as construction, manufacturing, and law enforcement.
21. How to Care for Your Uniforms
Proper care is essential for maintaining the appearance and longevity of your uniforms. Follow these tips to keep your uniforms looking their best.
21.1 Read the Care Label
Always read the care label before washing or drying your uniforms. The care label provides specific instructions for washing, drying, and ironing the garment.
21.2 Wash Uniforms Regularly
Wash uniforms regularly to remove dirt, stains, and odors. Follow the care label instructions for water temperature and detergent type.
21.3 Avoid Overloading the Washing Machine
Avoid overloading the washing machine, as this can prevent the uniforms from getting properly cleaned. Wash uniforms in small loads to ensure they are thoroughly cleaned.
22. Benefits of Buying Uniforms Online
Buying uniforms online offers several benefits, including convenience, selection, and price. With onlineuniforms.net, you can easily find the perfect uniforms for your business, school, or organization from the comfort of your own home.
22.1 Convenience
Buying uniforms online is convenient and saves time. You can browse our wide selection of uniforms, place your order, and have your uniforms delivered to your doorstep without ever leaving your home or office.
22.2 Wide Selection
Onlineuniforms.net offers a wide selection of uniforms in various styles, colors, and sizes. You can easily find the perfect uniforms to meet your specific needs and preferences.
22.3 Competitive Prices
We offer competitive prices on all of our uniforms. You can save money by buying uniforms online compared to buying them from a traditional retail store.
23. Tips for Choosing the Right Uniform Supplier
Choosing the right uniform supplier is essential for ensuring you get high-quality uniforms that meet your specific needs. Here are some tips for choosing the right uniform supplier:
23.1 Consider Reputation and Experience
Choose a uniform supplier with a good reputation and extensive experience in the industry. Look for suppliers with positive reviews and a track record of providing high-quality uniforms and excellent customer service.
23.2 Evaluate Product Quality
Evaluate the quality of the uniforms offered by the supplier. Look for uniforms made from durable materials that can withstand the rigors of daily wear and tear.
23.3 Assess Customization Options
Assess the customization options offered by the supplier. Choose a supplier that can provide the customization services you need, such as embroidery, screen printing, and heat transfer.
24. The Role of Uniforms in Creating a Safe Work Environment
Uniforms play a critical role in creating a safe work environment, particularly in industries such as construction, manufacturing, and healthcare.
24.1 Protective Clothing
Uniforms that include protective clothing, such as safety vests, hard hats, and gloves, can help protect employees from hazards in the workplace. These items can prevent injuries and save lives.
24.2 Identification
Uniforms can help identify employees and distinguish them from visitors or unauthorized personnel. This is particularly important in industries where security is a concern.
24.3 Hygiene
In industries such as healthcare and food service, uniforms can help maintain hygiene and prevent the spread of germs. Uniforms should be washed regularly and changed frequently to minimize the risk of contamination.
25. Uniforms as a Marketing Tool
Uniforms can serve as a powerful marketing tool, helping to promote your brand and attract new customers.
25.1 Brand Awareness
Uniforms with your company logo and colors can help increase brand awareness and visibility. When your employees wear branded uniforms in public, they act as walking billboards, promoting your brand to a wider audience.
25.2 Customer Recognition
Uniforms can help customers easily identify your employees and distinguish them from employees of other businesses. This can improve customer service and enhance the overall customer experience.
25.3 Professional Image
Uniforms can help create a professional and polished image for your business. When your employees wear branded uniforms, they project a sense of professionalism and credibility to your customers.
26. Overcoming Common Challenges in Uniform Management
Managing uniforms can be challenging, particularly for large organizations with many employees. Here are some common challenges and how to overcome them:
26.1 Sizing Issues
Sizing issues can be a major challenge in uniform management. To overcome this, provide employees with a detailed sizing guide and offer a range of sizes to accommodate different body types.
26.2 Inventory Management
Inventory management can be complex, particularly for organizations with a large number of uniforms. Use an inventory management system to track uniform levels and ensure you have enough uniforms on hand to meet demand.
26.3 Employee Compliance
Ensuring employee compliance with uniform policies can be challenging. Clearly communicate uniform policies to employees and enforce them consistently.
27. Order Your Uniforms Today at Onlineuniforms.net
Ready to upgrade your team’s look with high-quality and stylish uniforms? Visit onlineuniforms.net today to explore our wide selection of work apparel, professional clothing, and custom uniform options. Contact us at +1 (214) 651-8600 or visit our location at 1515 Commerce St, Dallas, TX 75201, United States. Let us help you create a professional and cohesive team image with our durable and affordable uniform solutions. Don’t wait – order your uniforms today and elevate your brand!
 Mechanic in blue uniform inspecting car engine
Mechanic in blue uniform inspecting car engine
FAQ: Is Kinetic Energy Constant in Uniform Circular Motion?
FAQ 1: What exactly is uniform circular motion?
Uniform circular motion describes an object moving at a constant speed along a circular path, where only direction changes but not the speed.
FAQ 2: Why doesn’t kinetic energy change in uniform circular motion?
Kinetic energy is dependent on the speed and mass of the object. In uniform circular motion, these variables stay constant; hence, kinetic energy remains constant.
FAQ 3: How does the work-energy theorem apply to uniform circular motion?
The work-energy theorem states that the change in kinetic energy equals the net work done on an object, and in uniform circular motion, no work is done; therefore, the kinetic energy does not change.
FAQ 4: Does centripetal force affect kinetic energy in circular motion?
Centripetal force does not change the kinetic energy because it acts perpendicular to the motion, doing zero work.
FAQ 5: Can external forces alter kinetic energy during circular motion?
Yes, external forces like friction can do work, altering the object’s speed and thus changing the kinetic energy.
FAQ 6: What role does angular velocity play in the kinetic energy of circular motion?
Kinetic energy can be expressed using angular velocity, showing that if angular velocity is constant, so is the kinetic energy, as long as the mass and radius are constant.
FAQ 7: Is kinetic energy constant in non-uniform circular motion?
No, because in non-uniform circular motion, the speed changes, leading to a change in kinetic energy.
FAQ 8: How do real-world examples reflect constant kinetic energy in uniform circular motion?
Examples include satellites orbiting the earth and CD players, where the rotation is constant and maintains uniform kinetic energy.
FAQ 9: What are the practical implications of understanding kinetic energy in uniform circular motion?
Understanding kinetic energy helps in designing machines and ensuring the safety of rotational systems by maintaining constant kinetic energy and minimizing energy losses.
FAQ 10: Where can I find durable and customizable uniforms online?
Visit onlineuniforms.net for a wide range of uniform options that include customization to elevate your brand.
