Are you looking to understand what uniform motion is and how it applies in real life? Uniform motion refers to an object moving in a straight line at a constant speed, and onlineuniforms.net is here to provide clarity and examples to help you grasp this concept. Discover how this principle works and explore related concepts like uniform circular motion.
1. Understanding Uniform Motion
What exactly is uniform motion, and why is it important?
Uniform motion is when an object moves in a straight line at a constant speed. This means its velocity remains unchanged over time, covering equal distances in equal intervals. Understanding uniform motion is crucial in physics as it forms the basis for analyzing more complex movements.
1.1. Defining Uniform Motion
How do we define uniform motion in physics?
Uniform motion is defined as the movement of an object along a straight path with a constant velocity. This implies that the object’s speed and direction remain unchanged throughout its motion. In simpler terms, the object covers the same distance in each unit of time.
1.2. Key Characteristics of Uniform Motion
What are the main characteristics that define uniform motion?
- Constant Velocity: The object’s speed and direction remain constant.
- Straight Path: The object moves along a straight line.
- Equal Distances: The object covers equal distances in equal intervals of time.
- Zero Acceleration: Since the velocity is constant, the acceleration is zero.
1.3. Importance of Understanding Uniform Motion
Why is it important to understand the concept of uniform motion?
Understanding uniform motion is fundamental because it serves as a building block for understanding more complex types of motion, such as non-uniform motion and accelerated motion. It provides a clear and simple model for analyzing movement, making it easier to predict and control the motion of objects. Additionally, uniform motion is essential in various real-world applications, including engineering, robotics, and transportation.
2. Real-World Examples of Uniform Motion
Can you give some real-world examples of uniform motion?
Many everyday scenarios demonstrate uniform motion. These examples help to illustrate the concept and make it more relatable.
2.1. Examples in Daily Life
Where can we observe uniform motion in our daily lives?
- A Car on Cruise Control: When a car is set on cruise control on a flat, straight highway, it maintains a constant speed, demonstrating uniform motion.
- An Airplane in Flight: An airplane flying at a constant altitude and speed in a straight line exhibits uniform motion.
- A Ball Rolling on a Flat Surface: If a ball is rolling on a perfectly flat surface with no friction or external forces, it would continue moving at a constant speed in a straight line.
- A Conveyor Belt: A conveyor belt moving at a constant speed transports items uniformly.
2.2. Examples in Sports
Are there examples of uniform motion in sports?
Yes, there are several instances where uniform motion can be observed in sports, although they are often idealized due to other factors influencing motion.
- Ice Skating: An ice skater gliding across the ice at a constant speed in a straight line approximates uniform motion.
- Swimming: A swimmer maintaining a constant speed and direction in a pool demonstrates uniform motion.
- Bowling: After the bowler releases the ball, if it travels down the lane at a consistent speed and straight path (before any curve or spin takes effect), it’s close to uniform motion.
2.3. Uniform Motion in Engineering
How is uniform motion applied in engineering?
Engineers use the principles of uniform motion in various applications to design and control systems.
- Robotics: Robots designed to move at a constant speed in a straight line, such as those used in manufacturing, rely on uniform motion.
- Transportation Systems: Designing trains and other vehicles to move at a consistent speed along a straight track involves understanding and applying uniform motion.
- Automation: Automated systems in factories, like assembly lines, utilize uniform motion to ensure consistent and efficient production.
 Car on Cruise Control
Car on Cruise Control
3. Understanding Non-Uniform Motion
What is non-uniform motion, and how does it differ from uniform motion?
Non-uniform motion occurs when an object’s velocity changes over time, either in speed or direction, or both. This is in contrast to uniform motion, where velocity remains constant.
3.1. Defining Non-Uniform Motion
How is non-uniform motion defined in physics?
Non-uniform motion is defined as the movement of an object where its velocity is not constant. This means the object’s speed, direction, or both are changing with time. Unlike uniform motion, non-uniform motion involves acceleration.
3.2. Key Characteristics of Non-Uniform Motion
What are the key characteristics that distinguish non-uniform motion?
- Changing Velocity: The object’s speed or direction changes over time.
- Acceleration: The object experiences acceleration, which can be positive (speeding up), negative (slowing down), or changing direction.
- Varied Distances: The object covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time.
- Curved Path: The object may move along a curved path, indicating a change in direction.
3.3. Examples of Non-Uniform Motion
Can you provide some examples of non-uniform motion?
- A Car Accelerating: When a car speeds up from a stop, its velocity is changing, indicating non-uniform motion.
- A Ball Thrown in the Air: The motion of a ball thrown upwards is non-uniform due to the influence of gravity, which causes it to slow down as it rises and speed up as it falls.
- A Train Starting or Stopping: A train’s motion is non-uniform when it starts from rest or when it applies brakes to come to a stop.
- Roller Coaster: A roller coaster involves dramatic changes in speed and direction, representing non-uniform motion.
4. Uniform Motion vs. Uniform Acceleration
What is the difference between uniform motion and uniform acceleration?
It’s common to confuse uniform motion with uniform acceleration, but they are distinct concepts.
4.1. Defining Uniform Acceleration
What is uniform acceleration, and how does it differ from uniform motion?
Uniform acceleration is defined as motion in which the velocity of an object changes at a constant rate. Unlike uniform motion, where velocity remains constant, uniform acceleration involves a steady increase or decrease in velocity over time.
4.2. Key Differences
What are the main differences between uniform motion and uniform acceleration?
| Feature | Uniform Motion | Uniform Acceleration |
|---|---|---|
| Velocity | Constant | Changing at a constant rate |
| Acceleration | Zero | Constant and non-zero |
| Distance | Equal distances in equal time intervals | Unequal distances in equal time intervals |
| Example | Car on cruise control | Car accelerating from a stop |
| Graph (Distance-Time) | Straight line | Curved line (parabola) |
4.3. Examples of Uniform Acceleration
Where can we observe uniform acceleration in real life?
- Free Fall: An object falling freely under the influence of gravity experiences uniform acceleration (ignoring air resistance).
- A Car Accelerating at a Constant Rate: If a car increases its speed by the same amount every second, it is undergoing uniform acceleration.
- An Object Sliding Down an Inclined Plane: An object sliding down a frictionless inclined plane experiences uniform acceleration due to the constant component of gravity.
- Elevators: Elevators maintain a constant rate of acceleration.
5. Uniform Circular Motion Explained
What is uniform circular motion, and how does it relate to uniform motion?
Uniform circular motion is a special type of motion where an object moves at a constant speed along a circular path.
5.1. Defining Uniform Circular Motion
How is uniform circular motion defined?
Uniform circular motion is defined as the movement of an object along a circular path at a constant speed. Although the speed is constant, the velocity is not, because the direction of motion is continuously changing.
5.2. Key Characteristics
What are the key characteristics of uniform circular motion?
- Constant Speed: The object moves at a constant speed.
- Circular Path: The object follows a circular trajectory.
- Changing Velocity: The direction of the velocity is constantly changing, resulting in continuous acceleration towards the center of the circle.
- Centripetal Acceleration: The object experiences centripetal acceleration, which is always directed towards the center of the circle.
5.3. Examples of Uniform Circular Motion
Can you give some examples of uniform circular motion?
- A Satellite Orbiting the Earth: A satellite orbiting the Earth at a constant altitude and speed exhibits uniform circular motion.
- A Car Moving Around a Circular Track: When a car moves around a circular track at a constant speed, it is in uniform circular motion.
- The Blades of a Ceiling Fan: The tips of the blades of a ceiling fan rotating at a constant speed undergo uniform circular motion.
- Merry-Go-Round: A child riding a merry-go-round maintains constant speed around a fixed axis.
6. Non-Uniform Circular Motion
What is non-uniform circular motion, and how does it differ from uniform circular motion?
Non-uniform circular motion occurs when an object moves along a circular path with a changing speed.
6.1. Defining Non-Uniform Circular Motion
How is non-uniform circular motion defined?
Non-uniform circular motion is defined as the movement of an object along a circular path where its speed varies. This means the object experiences both centripetal and tangential acceleration.
6.2. Key Characteristics
What are the key characteristics of non-uniform circular motion?
- Changing Speed: The object’s speed varies as it moves along the circular path.
- Circular Path: The object follows a circular trajectory.
- Tangential Acceleration: The object experiences tangential acceleration, which is responsible for the change in speed.
- Centripetal Acceleration: The object also experiences centripetal acceleration, which keeps it moving in a circle.
6.3. Examples of Non-Uniform Circular Motion
Can you provide some examples of non-uniform circular motion?
- A Roller Coaster Loop: A roller coaster moving through a loop experiences non-uniform circular motion because its speed changes as it goes up and down the loop.
- A Car Speeding Up Around a Curve: When a car accelerates while turning a corner, it exhibits non-uniform circular motion.
- Swinging a Ball on a String: If you swing a ball on a string and vary your speed, the ball undergoes non-uniform circular motion.
- Ferris Wheel: A Ferris wheel may change speed.

7. Graphing Uniform Motion
How can we represent uniform motion graphically?
Graphs are useful tools for visualizing and analyzing motion.
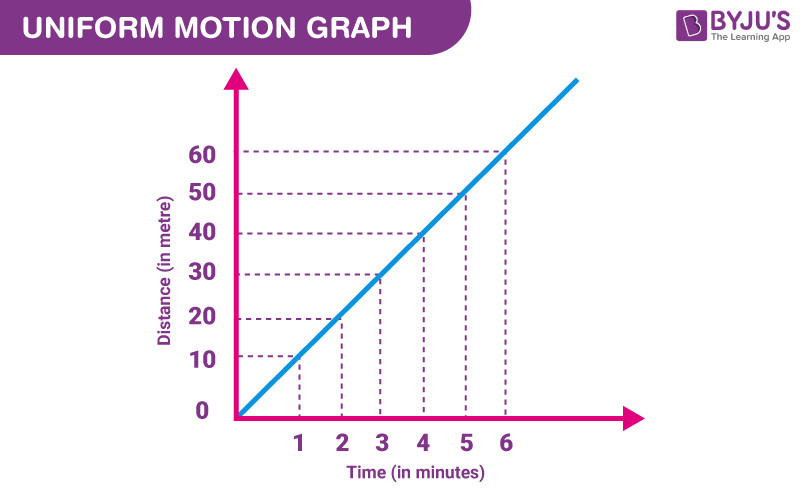
7.1. Distance-Time Graphs
What does a distance-time graph look like for uniform motion?
In a distance-time graph, uniform motion is represented by a straight line. The slope of the line indicates the speed of the object. A steeper slope means a higher speed, while a horizontal line indicates that the object is at rest.
7.2. Velocity-Time Graphs
How is uniform motion represented on a velocity-time graph?
In a velocity-time graph, uniform motion is represented by a horizontal line. This indicates that the velocity remains constant over time. The area under the line represents the displacement of the object.
7.3. Interpreting Graphs
How can we interpret these graphs to understand uniform motion?
- Distance-Time Graph:
- Straight Line: Indicates uniform motion.
- Slope: Represents the speed of the object.
- Horizontal Line: Indicates the object is at rest.
- Velocity-Time Graph:
- Horizontal Line: Indicates uniform motion with constant velocity.
- Area Under the Line: Represents the displacement of the object.
8. Formulas and Equations for Uniform Motion
What are the key formulas and equations used to describe uniform motion?
Understanding the formulas and equations associated with uniform motion is essential for solving problems and making calculations.
8.1. Key Formulas
What are the main formulas used in uniform motion calculations?
- Velocity (v): ( v = frac{d}{t} )
- Where ( d ) is the distance traveled and ( t ) is the time taken.
- Distance (d): ( d = v times t )
- This formula calculates the distance traveled when the velocity and time are known.
- Time (t): ( t = frac{d}{v} )
- This formula calculates the time taken when the distance and velocity are known.
8.2. Example Calculations
Can you provide some example calculations using these formulas?
- Example 1: A car travels at a constant speed of 20 m/s for 10 seconds. What distance does it cover?
- Using the formula ( d = v times t ), ( d = 20 text{ m/s} times 10 text{ s} = 200 text{ meters} ).
- Example 2: An object moves 150 meters at a constant speed of 5 m/s. How long does it take?
- Using the formula ( t = frac{d}{v} ), ( t = frac{150 text{ m}}{5 text{ m/s}} = 30 text{ seconds} ).
- Example 3: A runner covers 100 meters in 25 seconds at a constant speed. What is the runner’s speed?
- Using the formula ( v = frac{d}{t} ), ( v = frac{100 text{ m}}{25 text{ s}} = 4 text{ m/s} ).
8.3. Applying Formulas to Real-World Problems
How can we apply these formulas to solve real-world problems involving uniform motion?
These formulas are applicable in various scenarios:
- Transportation Planning: Calculating travel times and distances for vehicles moving at constant speeds.
- Sports Analysis: Analyzing the speed and distance covered by athletes in events like running or swimming.
- Engineering Design: Designing systems that require consistent and predictable motion, such as conveyor belts or automated machinery.
9. Practical Applications of Uniform Motion
How is uniform motion used in practical applications and industries?
The principles of uniform motion are applied in numerous fields to ensure efficiency and precision.
9.1. Applications in Manufacturing
How is uniform motion utilized in manufacturing processes?
- Assembly Lines: Uniform motion is crucial in assembly lines, where products move at a constant speed from one station to another, ensuring consistent production rates.
- Robotics: Robots performing repetitive tasks, such as welding or painting, often move at a constant speed along a defined path, demonstrating uniform motion.
- Conveyor Systems: Conveyor belts are used to transport materials and products at a constant speed, facilitating smooth and efficient material handling.
9.2. Applications in Transportation
How is uniform motion applied in transportation systems?
- Cruise Control Systems: Modern vehicles use cruise control to maintain a constant speed on highways, providing a practical example of uniform motion.
- Train Systems: Trains moving along straight tracks at a constant speed demonstrate uniform motion, optimizing travel times and energy efficiency.
- Aircraft Flight: Airplanes flying at a constant altitude and speed in a straight line rely on uniform motion principles to maintain stable and efficient flight.
9.3. Applications in Robotics
How do robots utilize uniform motion for various tasks?
- Automated Material Handling: Robots in warehouses and factories use uniform motion to move items from one location to another with precision and consistency.
- Precision Welding: Robots performing welding tasks move at a constant speed along the weld path, ensuring consistent and high-quality welds.
- Automated Painting: Robots applying paint or coatings move at a uniform speed to achieve even and consistent coverage.
10. Common Misconceptions About Uniform Motion
What are some common misconceptions about uniform motion, and how can we clarify them?
Several misconceptions can arise when learning about uniform motion.
10.1. Confusing Uniform Motion with Constant Motion
What is the difference between uniform motion and constant motion?
- Misconception: Uniform motion is often confused with constant motion, but they are not the same. Constant motion only implies constant speed, while uniform motion requires both constant speed and direction.
- Clarification: Uniform motion involves movement along a straight line at a constant speed. Constant motion can include changes in direction, such as circular motion at a constant speed, which is not uniform motion.
10.2. Assuming Uniform Motion Means No Forces Act on the Object
Does uniform motion mean that no forces are acting on the object?
- Misconception: Some believe that if an object is in uniform motion, no forces are acting on it.
- Clarification: Uniform motion implies that the net force acting on the object is zero. This does not mean that no forces are present, but rather that the forces are balanced. For example, a car moving at a constant speed on a highway experiences both forward force from the engine and opposing forces like air resistance and friction, which cancel each other out.
10.3. Thinking Uniform Motion Is Only Theoretical
Is uniform motion purely a theoretical concept with no real-world examples?
- Misconception: Uniform motion is often considered a theoretical concept with no practical applications.
- Clarification: While perfect uniform motion is difficult to achieve due to factors like friction and air resistance, many real-world scenarios approximate it closely enough for practical purposes. Examples include cruise control in cars, airplanes in stable flight, and conveyor belts in factories.
11. Advanced Concepts Related to Uniform Motion
What are some advanced concepts related to uniform motion?
To further expand your understanding, let’s explore some advanced concepts.
11.1. Inertial Frames of Reference
What are inertial frames of reference, and how do they relate to uniform motion?
- Definition: An inertial frame of reference is a frame in which an object not subject to any net external force is at rest or moves at a constant velocity in a straight line.
- Relevance: Uniform motion is a defining characteristic of inertial frames. Newton’s laws of motion are valid in inertial frames, making them essential for analyzing motion.
11.2. Galilean Relativity
What is Galilean relativity, and how does it build on the concept of uniform motion?
- Definition: Galilean relativity states that the laws of physics are the same in all inertial frames of reference. This means that the outcome of any mechanical experiment performed in a uniformly moving system will be the same as if it were performed at rest.
- Relevance: Galilean relativity builds on the concept of uniform motion by showing that motion is relative and depends on the observer’s frame of reference.
11.3. Applications in Space Travel
How is uniform motion relevant to space travel and celestial mechanics?
- Spacecraft Motion: Once a spacecraft is in space and far from significant gravitational influences, it can travel at a constant velocity in a straight line, demonstrating uniform motion.
- Orbital Mechanics: While orbits are generally elliptical, understanding uniform circular motion provides a basis for analyzing the motion of celestial bodies and spacecraft.
12. How Onlineuniforms.net Can Help
Are you looking for high-quality uniforms that ensure your team looks professional and moves with ease?
At onlineuniforms.net, we understand the importance of comfortable and functional uniforms. Whether you need uniforms for healthcare, education, or corporate settings, our range of products is designed to meet your specific needs.
12.1. Wide Range of Uniform Options
What types of uniforms does onlineuniforms.net offer?
We provide a variety of uniforms, including:
- Medical Scrubs: Comfortable and durable scrubs for healthcare professionals.
- School Uniforms: High-quality uniforms for students of all ages.
- Corporate Attire: Professional attire that reflects your brand identity.
- Custom Uniforms: Tailored uniforms to meet your specific requirements.
12.2. Customization Services
Can onlineuniforms.net customize uniforms with logos and designs?
Yes, we offer customization services to add your company logo, employee names, and other unique designs to your uniforms. Our customization options include embroidery, screen printing, and heat transfer.
12.3. Quality and Durability
How does onlineuniforms.net ensure the quality and durability of its uniforms?
We use high-quality materials and advanced manufacturing techniques to ensure that our uniforms are durable, comfortable, and long-lasting. Our products are designed to withstand the rigors of daily wear and tear.
12.4. Easy Ordering Process
How can I order uniforms from onlineuniforms.net?
Ordering from onlineuniforms.net is easy and convenient. Simply visit our website, browse our catalog, select the items you need, and place your order online. Our customer service team is available to assist you with any questions or concerns.
13. FAQs About Uniform Motion
Let’s address some frequently asked questions about uniform motion.
13.1. What Is the SI Unit for Velocity in Uniform Motion?
What unit of measurement is used for velocity in uniform motion?
The SI unit for velocity in uniform motion is meters per second (m/s). This unit expresses the distance traveled in meters per unit of time in seconds.
13.2. Can Uniform Motion Occur in a Curved Path?
Is it possible for uniform motion to occur along a curved path?
No, uniform motion can only occur along a straight path. If an object is moving along a curved path, its direction is constantly changing, which means its velocity is not constant, thus it’s not uniform motion.
13.3. What Is the Acceleration in Uniform Motion?
What is the value of acceleration in uniform motion?
The acceleration in uniform motion is always zero because the velocity remains constant. Since acceleration is the rate of change of velocity, a constant velocity implies no acceleration.
13.4. How Does Friction Affect Uniform Motion?
How does friction affect an object in uniform motion?
Friction opposes motion and causes an object to slow down. If friction is present, the object will not maintain a constant velocity unless an external force is applied to counteract the friction. Therefore, friction tends to disrupt uniform motion.
13.5. What Is the Importance of Uniform Motion in Physics?
Why is the concept of uniform motion important in physics?
Uniform motion is a fundamental concept in physics because it provides a simple model for analyzing movement. It serves as a basis for understanding more complex types of motion and is essential in various applications, including engineering, robotics, and transportation.
13.6. How Do We Calculate Average Speed in Uniform Motion?
How is average speed calculated in uniform motion?
In uniform motion, the average speed is equal to the constant speed of the object. It is calculated by dividing the total distance traveled by the total time taken: ( text{Average Speed} = frac{text{Total Distance}}{text{Total Time}} ).
13.7. Can Air Resistance Affect Uniform Motion?
Can air resistance impact an object’s ability to maintain uniform motion?
Yes, air resistance can significantly affect uniform motion. Air resistance is a force that opposes the motion of an object through the air, causing it to slow down. To maintain uniform motion in the presence of air resistance, an equal and opposite force must be applied to counteract it.
13.8. What Happens If the Velocity Is Not Constant?
What type of motion occurs if the velocity of an object is not constant?
If the velocity of an object is not constant, the motion is called non-uniform motion. This means the object is either speeding up, slowing down, or changing direction.
13.9. Is Uniform Motion Possible in Real-World Scenarios?
To what extent can uniform motion be observed in real-world scenarios?
While perfect uniform motion is difficult to achieve in real-world scenarios due to factors like friction and air resistance, many situations approximate it closely enough for practical purposes. Examples include a car on cruise control on a flat highway or an airplane flying at a constant altitude and speed.
13.10. What Are the Real-World Applications of Uniform Motion?
In what real-world fields is the concept of uniform motion most applied?
The concept of uniform motion is applied in various real-world fields, including transportation, manufacturing, robotics, and sports analysis. It is used to design and control systems that require consistent and predictable motion.
Conclusion
Understanding uniform motion is essential for grasping fundamental physics concepts and their applications in the real world. From cruise control in cars to assembly lines in factories, uniform motion plays a crucial role in our daily lives.
Are you ready to outfit your team with high-quality, customized uniforms? Visit onlineuniforms.net today to explore our wide range of options and discover how we can help you achieve a professional and cohesive look. Contact us at +1 (214) 651-8600 or visit our location at 1515 Commerce St, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, and let us assist you in finding the perfect uniforms for your needs.
