Are you seeking clarity on what constitutes an element uniform throughout? This article, brought to you by onlineuniforms.net, will comprehensively address this topic, exploring the defining characteristics, applications, and advantages of elements with uniform properties, especially in the context of selecting the right materials for your online uniform needs. We aim to simplify complex concepts and provide insights into homogeneous elements.
1. What Does It Mean for an Element to Be Uniform Throughout?
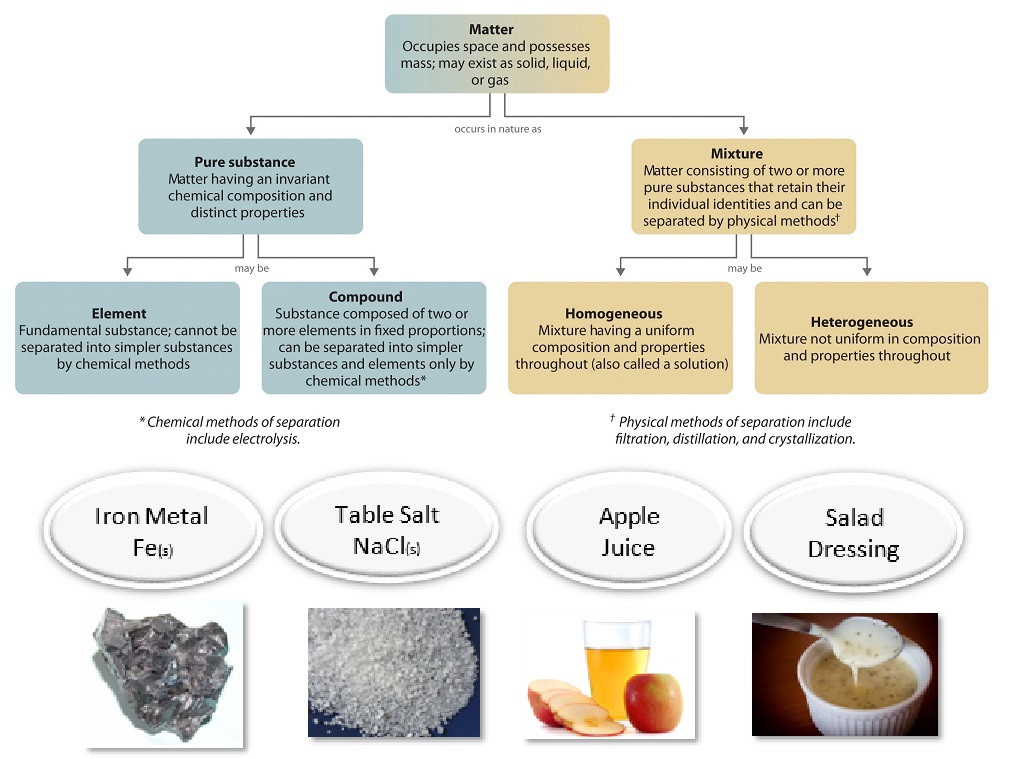
Yes, an element is uniform throughout because it consists of only one type of atom, meaning its composition and properties are consistent at any point within the substance. This uniformity is a fundamental characteristic of elements, distinguishing them from compounds and mixtures.
Exploring Uniformity at the Atomic Level
The essence of uniformity in an element lies in its atomic structure. Each element, such as gold (Au), silver (Ag), or oxygen (O2), is composed exclusively of identical atoms. This means that every part of a pure gold sample, for instance, will have the exact same chemical properties because it’s made of nothing but gold atoms.
Contrasting Elements with Compounds and Mixtures
To better understand this, let’s compare elements with compounds and mixtures:
- Compounds: These are formed when two or more different elements are chemically bonded together. For example, water (H2O) is a compound made of hydrogen and oxygen. Unlike elements, compounds can be broken down into simpler substances.
- Mixtures: These involve the physical combination of two or more substances (elements or compounds) that are not chemically bonded. Mixtures can be homogeneous (uniform throughout, like saltwater) or heterogeneous (non-uniform, like vegetable soup).
Real-World Examples of Uniform Elements
Consider these examples to see how uniformity applies in everyday life:
- Copper Wiring: Copper (Cu) is used in electrical wiring because of its excellent conductivity. The consistent atomic structure ensures that electricity flows evenly throughout the wire.
- Aluminum Foil: Aluminum (Al) is used for food packaging due to its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. Its uniform composition ensures that it provides a consistent barrier.
- Gold Jewelry: Gold (Au) is prized for its luster and resistance to tarnish. The uniformity of gold ensures that the jewelry maintains its appearance over time.
 Copper Wiring
Copper Wiring
Significance of Uniformity in Manufacturing
In manufacturing, the uniformity of elements is crucial for ensuring consistent product quality. For instance, in the production of semiconductors, elements like silicon (Si) must be exceptionally pure and uniform to function correctly.
2. How Do Elements Differ from Compounds in Terms of Uniformity?
Elements are inherently uniform, being composed of only one type of atom, whereas compounds consist of two or more different elements chemically bonded together, making them uniform in composition but breakable into simpler substances. This distinction is essential in understanding the nature of matter and its applications.
Atomic Composition: The Core Difference
The key to understanding the difference in uniformity lies in the atomic composition:
- Elements: Consist of a single type of atom. For example, a piece of iron (Fe) is made up of only iron atoms.
- Compounds: Consist of two or more types of atoms chemically bonded in a fixed ratio. For example, carbon dioxide (CO2) is made up of carbon and oxygen atoms in a 1:2 ratio.
Uniformity in Composition vs. Breakability
- Elements: Cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. This inherent simplicity ensures they are uniform throughout.
- Compounds: Can be broken down into simpler substances (elements) through chemical reactions. While the composition of a specific compound is uniform (e.g., every molecule of water is H2O), the compound itself is not an element and can be altered.
Examples to Illustrate the Difference
- Gold (Au): An element that is uniform throughout. You cannot break it down into simpler substances without changing its fundamental nature.
- Water (H2O): A compound that is uniform in its composition – every water molecule consists of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. However, through electrolysis, water can be broken down into hydrogen and oxygen gases.
- Sodium Chloride (NaCl): Commonly known as table salt, this compound is made of sodium and chlorine. It has a fixed composition, but it can be separated into its constituent elements through chemical processes.
Implications for Material Properties
The uniformity of elements leads to predictable and consistent properties, which is why they are often used in applications requiring high precision. Compounds, while uniform in their specific composition, can exhibit more varied properties depending on the elements they are made of and how these elements are bonded.
The Role of onlineuniforms.net
Understanding these differences is crucial when selecting materials for uniforms. Whether you need the durability of a uniform made from a specific element or the tailored properties of a compound-based fabric, onlineuniforms.net offers a range of options to meet your needs.
3. What Role Does Uniformity Play in the Properties of Elements?
Uniformity in elements dictates consistent physical and chemical properties, such as melting point, boiling point, density, and reactivity, making them predictable and reliable in various applications. This consistency is crucial for industries relying on specific material behaviors.
Consistent Physical Properties
Because elements are made of only one type of atom, their physical properties are highly consistent:
- Melting Point: The temperature at which a solid element turns into a liquid is constant throughout the substance. For example, pure gold melts at 1064°C (1947°F) regardless of the sample size.
- Boiling Point: Similarly, the temperature at which a liquid element turns into a gas is also constant. For example, liquid nitrogen boils at -196°C (-320°F) under normal atmospheric pressure.
- Density: The mass per unit volume of an element is consistent. For instance, the density of pure aluminum is always around 2.7 g/cm³.
- Electrical Conductivity: Elements like copper and silver have high and consistent electrical conductivity, making them ideal for electrical wiring.
Predictable Chemical Properties
The chemical behavior of elements is also highly predictable due to their uniformity:
- Reactivity: Elements react in predictable ways with other substances. For example, sodium (Na) reacts vigorously with water, while gold (Au) is highly inert and does not react with most substances.
- Oxidation: The tendency of an element to lose electrons (oxidize) is consistent. Iron (Fe) readily oxidizes to form rust in the presence of oxygen and moisture.
- Bonding: Elements form bonds with other elements in predictable ratios based on their valence electrons. This is why compounds have fixed compositions.
Impact on Industrial Applications
The consistent properties of elements are essential in various industries:
- Electronics: Silicon (Si) is used in semiconductors due to its consistent electrical properties, which are critical for the performance of electronic devices.
- Construction: Iron (Fe) and aluminum (Al) are used in construction because of their strength and consistent mechanical properties.
- Jewelry: Gold (Au) and platinum (Pt) are used in jewelry due to their inertness and consistent aesthetic properties.
Importance for Uniform Manufacturing at onlineuniforms.net
At onlineuniforms.net, understanding the role of uniformity in material properties is crucial for selecting the right fabrics and components for uniforms. Whether it’s the consistent color of a dyed fabric or the reliable strength of a specific fiber, uniformity ensures that the final product meets the required standards of quality and performance.
4. How Does a Homogeneous Mixture Differ from an Element in Terms of Uniformity?
A homogeneous mixture exhibits uniformity at a macroscopic level, meaning its composition appears consistent throughout, but it still contains multiple substances. An element, however, is uniform at the atomic level, composed of only one type of atom, offering a fundamental level of purity and consistency.
Understanding Homogeneous Mixtures
A homogeneous mixture is a combination of two or more substances where the composition is uniform throughout. This means that if you take a sample from any part of the mixture, it will have the same proportion of components.
- Examples of Homogeneous Mixtures:
- Saltwater: Salt (sodium chloride) dissolved in water.
- Air: A mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and other gases.
- Vinegar: Acetic acid dissolved in water.
Uniformity in Homogeneous Mixtures
The uniformity in a homogeneous mixture is at the macroscopic level. While the substances are evenly distributed, they are still distinct entities. For instance, in saltwater, you have water molecules and sodium chloride molecules evenly dispersed, but they remain separate molecules.
Elements: Uniformity at the Atomic Level
In contrast, an element is uniform at the atomic level. It is composed of only one type of atom, ensuring that every part of the element has the same fundamental properties.
- Examples of Elements:
- Gold (Au): Composed of only gold atoms.
- Copper (Cu): Composed of only copper atoms.
- Oxygen (O2): Composed of only oxygen atoms.
Key Differences in Uniformity
| Feature | Homogeneous Mixture | Element |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Two or more substances evenly distributed | Only one type of atom |
| Level of Uniformity | Macroscopic (appears uniform to the naked eye) | Atomic (uniform at the fundamental level) |
| Separability | Can be separated into its components by physical means | Cannot be broken down by chemical or physical means without changing its identity |
| Examples | Saltwater, air, vinegar | Gold, copper, oxygen |
Implications for Practical Applications
- Purity and Consistency: Elements are used when high purity and consistent properties are required. For example, silicon in semiconductors must be extremely pure to function correctly.
- Versatility: Homogeneous mixtures are used when a combination of properties is needed. For example, various alloys (homogeneous mixtures of metals) are designed for specific strength and corrosion resistance.
Application at onlineuniforms.net
At onlineuniforms.net, we consider these distinctions when sourcing materials for uniforms. Whether it’s the choice of a pure fiber for hypoallergenic properties or a blended fabric for enhanced durability, understanding the level of uniformity helps us deliver quality and performance.
5. What Are Some Examples of Elements That Must Be Uniform for Specific Applications?
Several elements require strict uniformity for specific applications, including silicon in semiconductors, gold in electronics, and platinum in catalytic converters, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in their respective fields.
Silicon in Semiconductors
- Why Uniformity is Crucial: Silicon (Si) is the backbone of the semiconductor industry. Its electrical properties are highly dependent on its purity and uniformity. Even tiny amounts of impurities can drastically alter its conductivity, rendering it useless for electronic devices.
- Application: Used in transistors, integrated circuits, and microchips.
- Requirements: Semiconductor-grade silicon must have a purity level of 99.9999999% (referred to as “nine nines” purity). The uniformity ensures that the electrical conductivity is consistent across the entire chip, allowing for reliable and predictable performance.
Gold in Electronics
- Why Uniformity is Crucial: Gold (Au) is used in electronics because of its excellent electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion. Uniformity ensures that the gold plating or wiring maintains its conductivity over time, even in harsh environments.
- Application: Used in connectors, printed circuit boards, and electrical contacts.
- Requirements: Gold used in electronics must be highly pure and free from contaminants. Any impurities can increase resistance and lead to failure. Uniformity in the gold layer ensures consistent performance and longevity.
Platinum in Catalytic Converters
- Why Uniformity is Crucial: Platinum (Pt) is a key component in catalytic converters, which are used to reduce harmful emissions from vehicles. The catalytic activity of platinum depends on its surface area and uniform distribution within the converter.
- Application: Used in automotive catalytic converters to convert carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides into less harmful substances.
- Requirements: Platinum must be uniformly dispersed on a support material (usually alumina) to maximize its catalytic activity. Uniformity ensures that the conversion process is efficient and meets emission standards.
Other Examples
- Aluminum in Aerospace: Aluminum (Al) alloys used in aerospace applications require high uniformity to ensure consistent strength and resistance to fatigue.
- Copper in Electrical Wiring: Copper (Cu) used in electrical wiring must be highly pure and uniform to ensure efficient and safe transmission of electricity.
- Titanium in Medical Implants: Titanium (Ti) used in medical implants must be biocompatible and uniform to prevent adverse reactions and ensure long-term stability.
The Role of Quality Control
Achieving uniformity in these elements requires rigorous quality control processes, including:
- Purification Techniques: Methods such as zone refining and chemical vapor deposition are used to purify elements to the required levels.
- Analytical Testing: Techniques like mass spectrometry and X-ray diffraction are used to verify the purity and uniformity of the elements.
Uniforms and Material Consistency at onlineuniforms.net
At onlineuniforms.net, we understand the importance of material consistency for uniform performance. We ensure that the fabrics and components we use meet stringent quality standards, providing our customers with reliable and durable uniforms.
6. What Manufacturing Processes Ensure an Element is Uniform Throughout?
Several manufacturing processes ensure elemental uniformity, including zone refining, Czochralski process, and powder metallurgy, each designed to eliminate impurities and ensure consistent composition throughout the material.
Zone Refining
Zone refining is a method used to purify elements, particularly semiconductors like silicon and germanium. It involves melting a small section (zone) of a solid material and slowly moving this molten zone along the length of the material. Impurities tend to concentrate in the molten zone and are swept to one end of the material, leaving behind a highly purified substance.
- Process:
- A solid rod of the element is placed in a furnace.
- A small section of the rod is melted using a heater.
- The heater slowly moves along the rod, causing the molten zone to travel from one end to the other.
- Impurities concentrate in the molten zone and are carried to the end of the rod.
- The process is repeated multiple times to achieve higher purity levels.
- Result: The purified material has a uniform composition with minimal impurities.
Czochralski Process
The Czochralski process is used to grow large, single-crystal ingots of elements like silicon. These ingots are then sliced into wafers for use in semiconductors. The process involves dipping a seed crystal into a crucible of molten element and slowly pulling it upwards while rotating. As the crystal is pulled, the molten material solidifies onto the seed crystal, forming a large, uniform crystal.
- Process:
- A crucible is filled with the element to be purified and heated until it melts.
- A seed crystal of the same element is dipped into the molten material.
- The seed crystal is slowly pulled upwards while rotating.
- As the crystal is pulled, the molten material solidifies onto the seed, forming a large single crystal.
- Result: The resulting crystal has a highly uniform composition and crystal structure.
Powder Metallurgy
Powder metallurgy is a process used to create parts from metal powders. The powders are compacted into a desired shape and then heated (sintered) to bond the particles together. This process can be used to create materials with a uniform composition by carefully controlling the composition of the starting powders.
- Process:
- Metal powders of the desired composition are mixed together.
- The powder mixture is compacted into a mold using high pressure.
- The compacted part is heated in a controlled atmosphere to sinter the particles together.
- Result: The resulting part has a uniform composition and density.
Other Techniques
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Used to deposit thin films of elements with high uniformity.
- Electrolysis: Used to purify metals by selectively dissolving and depositing them onto electrodes.
Importance of Controlled Environments
All these processes require carefully controlled environments to prevent contamination and ensure uniformity. Factors such as temperature, pressure, and atmosphere must be precisely controlled to achieve the desired results.
Application at onlineuniforms.net
At onlineuniforms.net, we work with suppliers who utilize these advanced manufacturing processes to ensure that the materials used in our uniforms are of the highest quality and uniformity. This commitment to quality helps us deliver uniforms that meet the needs of our customers.
7. How Does Uniformity in Elements Affect Their Use in Electronic Devices?
Uniformity is paramount in elements used in electronic devices, ensuring consistent electrical conductivity, thermal stability, and overall reliability, all critical for optimal device performance.
Consistent Electrical Conductivity
- Impact of Uniformity: In electronic devices, elements like copper, gold, and aluminum are used for their excellent electrical conductivity. The uniformity of these elements ensures that the flow of electricity is consistent and predictable throughout the device.
- Why It Matters: Variations in composition or the presence of impurities can create resistance, leading to energy loss and reduced performance.
- Example: Copper wires used in circuits must be highly pure and uniform to ensure efficient transmission of electrical signals.
Thermal Stability
- Impact of Uniformity: Electronic devices generate heat during operation. Uniform elements exhibit consistent thermal expansion and heat dissipation, which is crucial for maintaining stable performance.
- Why It Matters: Non-uniform elements can lead to localized hotspots, causing thermal stress and potential device failure.
- Example: Silicon in semiconductors must have uniform thermal properties to prevent overheating and ensure reliable operation.
Reliability and Longevity
- Impact of Uniformity: The reliability of electronic devices depends on the consistent behavior of their components over time. Uniform elements are less prone to corrosion, oxidation, and other degradation processes.
- Why It Matters: Impurities and variations in composition can create weak points, leading to premature failure.
- Example: Gold connectors used in electronic devices must be highly pure and uniform to resist corrosion and maintain a reliable connection over the device’s lifespan.
Specific Examples
- Silicon in Transistors: Uniformity in silicon ensures that transistors switch on and off reliably, enabling the precise control of electrical signals.
- Gold in Connectors: Uniformity in gold connectors ensures a stable and low-resistance connection, preventing signal loss and ensuring reliable data transmission.
- Aluminum in Heat Sinks: Uniformity in aluminum heat sinks ensures efficient heat dissipation, preventing overheating and protecting sensitive components.
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
To achieve the required levels of uniformity, electronic device manufacturers use advanced techniques such as:
- Zone Refining: To purify elements to extremely high levels.
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): To deposit thin films of uniform composition.
- Sputtering: To create uniform coatings of metals and other materials.
Ensuring Quality at onlineuniforms.net
While onlineuniforms.net focuses on uniforms, we understand the importance of material quality and uniformity in all industries. We partner with suppliers who adhere to strict quality control standards, ensuring that our products meet the highest levels of performance and durability.
8. What Role Does Uniformity Play in the Strength and Durability of Materials?
Uniformity significantly enhances the strength and durability of materials by ensuring consistent stress distribution, minimizing weak points, and improving resistance to corrosion and fatigue, essential for long-lasting performance.
Consistent Stress Distribution
- Impact of Uniformity: When a material is subjected to stress (e.g., tension, compression, bending), the stress is distributed evenly throughout the material if it is uniform.
- Why It Matters: Non-uniform materials have weak points where stress concentrates, leading to premature failure.
- Example: Steel used in bridges must be uniform in composition and structure to ensure that it can withstand the loads placed upon it without failing.
Minimizing Weak Points
- Impact of Uniformity: Uniform materials have fewer defects, such as voids, cracks, or inclusions, which can act as stress concentrators and reduce strength.
- Why It Matters: The absence of weak points ensures that the material can withstand higher stresses before failing.
- Example: Aluminum alloys used in aircraft construction must be free from defects to ensure the structural integrity of the aircraft.
Resistance to Corrosion and Fatigue
- Impact of Uniformity: Uniform materials are more resistant to corrosion and fatigue because they have a consistent surface and internal structure.
- Why It Matters: Non-uniform materials can have areas that are more susceptible to corrosion or fatigue, leading to premature failure.
- Example: Stainless steel used in marine applications must be uniform in composition to resist corrosion from saltwater.
Specific Examples
- Metals: Uniform metals, such as steel and aluminum, are used in construction, transportation, and manufacturing because of their strength and durability.
- Ceramics: Uniform ceramics are used in high-temperature applications, such as engine components and cutting tools, because of their strength and resistance to wear.
- Polymers: Uniform polymers are used in a variety of applications, such as packaging, textiles, and medical devices, because of their flexibility and durability.
Manufacturing Techniques
To achieve uniformity in materials, manufacturers use techniques such as:
- Alloying: To create uniform mixtures of metals with enhanced properties.
- Heat Treatment: To modify the microstructure of materials and improve their strength and durability.
- Casting and Forging: To create parts with uniform shape and structure.
Importance for Uniforms at onlineuniforms.net
At onlineuniforms.net, we understand that the strength and durability of uniforms are essential for their long-lasting performance. We carefully select materials that are uniform in composition and structure, ensuring that our uniforms can withstand the rigors of daily wear and tear.
9. How Does the Concept of Uniformity Apply to Alloys and Composites?
In alloys and composites, uniformity refers to the even distribution of constituent materials, ensuring consistent properties and performance, though the specific requirements differ based on the material type.
Alloys
An alloy is a mixture of two or more elements, typically metals, that are combined to enhance specific properties. The concept of uniformity in alloys refers to the even distribution of the constituent elements throughout the material.
- Why Uniformity Matters:
- Consistent Properties: Uniform distribution ensures that the alloy has consistent mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties throughout.
- Enhanced Performance: Uniformity minimizes weak points and stress concentrations, leading to improved strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion.
- Examples:
- Steel: An alloy of iron and carbon, with other elements added to enhance specific properties. Uniform distribution of carbon and other alloying elements ensures consistent strength and hardness.
- Brass: An alloy of copper and zinc. Uniform distribution of zinc in the copper matrix ensures consistent color and corrosion resistance.
Composites
A composite material is made from two or more constituent materials with significantly different physical or chemical properties that, when combined, produce a material with characteristics different from the individual components. Uniformity in composites refers to the even distribution of the reinforcing material (e.g., fibers) within the matrix material (e.g., resin).
- Why Uniformity Matters:
- Strength and Stiffness: Uniform distribution of reinforcing fibers ensures that the composite has consistent strength and stiffness in all directions.
- Load Distribution: Uniformity allows the composite to distribute loads evenly, preventing stress concentrations and improving overall performance.
- Examples:
- Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP): Carbon fibers are embedded in a polymer matrix. Uniform distribution of the fibers ensures high strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness.
- Fiberglass: Glass fibers are embedded in a resin matrix. Uniform distribution of the fibers ensures good strength and impact resistance.
Manufacturing Techniques
To achieve uniformity in alloys and composites, manufacturers use a variety of techniques, including:
- Melting and Mixing: For alloys, the constituent elements are melted together and thoroughly mixed to ensure a homogeneous distribution.
- Lay-up Techniques: For composites, reinforcing fibers are carefully arranged within the matrix material to achieve a uniform distribution.
- Molding Processes: Techniques like resin transfer molding (RTM) and vacuum-assisted resin transfer molding (VARTM) are used to ensure uniform impregnation of the fibers with the matrix material.
Implications for Uniforms
At onlineuniforms.net, we leverage the principles of uniformity in alloys and composites to select materials that offer the best combination of properties for our uniforms. Whether it’s a blended fabric for enhanced durability or a composite material for specialized protection, we ensure that our materials meet the highest standards of quality and performance.
10. Where Can Businesses in the USA Find Uniforms Made with High Uniformity Standards?
Businesses in the USA seeking uniforms made with high uniformity standards can find reliable solutions at onlineuniforms.net, offering a wide range of customizable options, quality materials, and expert guidance.
Why Uniformity Standards Matter for Businesses
- Professional Appearance: Uniforms made with high uniformity standards ensure a consistent and professional look for all employees, enhancing brand image and customer trust.
- Durability and Longevity: Uniform materials with uniform composition and structure are more resistant to wear and tear, corrosion, and fading, extending the lifespan of the uniforms and reducing replacement costs.
- Employee Comfort and Safety: Uniformity in materials ensures consistent comfort and performance, enhancing employee satisfaction and productivity. Uniforms with uniform protective properties, such as flame resistance or chemical resistance, provide reliable protection for employees in hazardous environments.
How onlineuniforms.net Delivers High Uniformity Standards
- Quality Materials: We source our fabrics and components from reputable suppliers who adhere to strict quality control standards and use advanced manufacturing techniques to ensure uniformity.
- Customization Options: We offer a wide range of customization options, including fabric selection, color matching, and logo placement, allowing businesses to create uniforms that perfectly reflect their brand identity.
- Expert Guidance: Our team of uniform experts provides personalized assistance to help businesses select the right uniforms for their specific needs, taking into account factors such as industry requirements, employee comfort, and budget constraints.
Benefits of Choosing onlineuniforms.net
- Wide Selection: We offer a diverse selection of uniforms for various industries, including healthcare, hospitality, education, and manufacturing.
- Competitive Pricing: We provide competitive pricing without compromising on quality, helping businesses save money on their uniform purchases.
- Reliable Service: We are committed to providing excellent customer service and timely delivery, ensuring a smooth and hassle-free experience for our clients.
Call to Action
If you are a business in the USA looking for uniforms made with high uniformity standards, visit onlineuniforms.net today to explore our wide range of customizable options and request a quote. Contact us at +1 (214) 651-8600 or visit our location at 1515 Commerce St, Dallas, TX 75201, United States. Let us help you create uniforms that enhance your brand image, improve employee comfort, and provide lasting value.
FAQ: Understanding Uniformity in Elements
1. What does it mean for an element to be uniform throughout?
It means the element consists of only one type of atom, ensuring consistent composition and properties at any point within the substance. This uniformity is a defining characteristic of elements, differentiating them from compounds and mixtures.
2. How are elements different from compounds in terms of uniformity?
Elements are uniform due to being composed of only one type of atom, while compounds consist of two or more different elements chemically bonded together, making them uniform in composition but breakable into simpler substances. This distinction is vital in understanding the nature of matter.
3. What role does uniformity play in the properties of elements?
Uniformity dictates consistent physical and chemical properties like melting point, boiling point, density, and reactivity, making elements predictable and reliable in various applications. This consistency is crucial for industries relying on specific material behaviors.
4. How does a homogeneous mixture differ from an element in terms of uniformity?
A homogeneous mixture exhibits uniformity at a macroscopic level, appearing consistent throughout but still containing multiple substances. An element is uniform at the atomic level, composed of only one type of atom, offering a fundamental level of purity and consistency.
5. Can you give examples of elements that must be uniform for specific applications?
Yes, silicon in semiconductors, gold in electronics, and platinum in catalytic converters require strict uniformity for optimal performance and reliability. These elements’ properties depend heavily on their purity.
6. What manufacturing processes ensure an element is uniform throughout?
Zone refining, the Czochralski process, and powder metallurgy are designed to eliminate impurities and ensure consistent composition throughout the material. These processes ensure high purity.
7. How does uniformity in elements affect their use in electronic devices?
Uniformity ensures consistent electrical conductivity, thermal stability, and reliability, all critical for optimal device performance. Inconsistent elements can cause device failure.
8. What role does uniformity play in the strength and durability of materials?
Uniformity enhances strength and durability by ensuring consistent stress distribution, minimizing weak points, and improving resistance to corrosion and fatigue. Uniform materials perform better under stress.
9. How does the concept of uniformity apply to alloys and composites?
In alloys and composites, uniformity refers to the even distribution of constituent materials, ensuring consistent properties and performance, though the specific requirements differ based on the material type. Even distribution is key.
10. Where can businesses in the USA find uniforms made with high uniformity standards?
Businesses in the USA seeking uniforms made with high uniformity standards can find reliable solutions at onlineuniforms.net, offering customizable options, quality materials, and expert guidance. Businesses can contact onlineuniforms.net for more information.


