Are you looking for clarification on tangential acceleration within uniform circular motion? At onlineuniforms.net, we understand the importance of accuracy in physics and its applications. This article will explore whether tangential acceleration remains constant during uniform circular motion, providing a detailed explanation and addressing common queries.
1. What is Uniform Circular Motion?
Uniform circular motion refers to the movement of an object along a circular path with a constant speed. This means the object covers the same distance in the same amount of time throughout its journey around the circle. However, while the speed remains constant, the velocity is continuously changing because velocity is a vector quantity and includes direction, which changes constantly in circular motion.
1.1 Key Characteristics of Uniform Circular Motion
- Constant Speed: The object moves at a steady pace around the circle.
- Changing Velocity: The direction of the object’s motion is always changing.
- Centripetal Acceleration: An acceleration directed towards the center of the circle, necessary to keep the object moving in a circular path.
2. Understanding Tangential Acceleration
Tangential acceleration is the component of acceleration responsible for changes in the speed of an object moving along a curved path. It acts tangentially to the circle, either increasing or decreasing the object’s speed.
2.1 How Tangential Acceleration Works
- Increasing Speed: When tangential acceleration is in the direction of motion, the object speeds up.
- Decreasing Speed: When tangential acceleration is opposite to the direction of motion, the object slows down.
- Constant Speed: When tangential acceleration is zero, the object maintains a constant speed.
3. Is Tangential Acceleration Constant in Uniform Circular Motion?
No, tangential acceleration is not constant in uniform circular motion; it is zero.
In uniform circular motion, the defining characteristic is that the speed of the object remains constant. Since tangential acceleration is the rate of change of speed, and the speed is not changing, the tangential acceleration is zero. All the acceleration in uniform circular motion is directed towards the center of the circle and is known as centripetal acceleration.
3.1 Why Tangential Acceleration is Zero
- Definition of Uniform Motion: Uniform motion implies constant speed.
- Tangential Acceleration and Speed: Tangential acceleration measures the rate of change of speed.
- No Change in Speed: In uniform circular motion, there is no change in speed, hence no tangential acceleration.
4. Centripetal Acceleration in Uniform Circular Motion
Centripetal acceleration is the acceleration that causes an object to move in a circular path. It is always directed towards the center of the circle and is essential for maintaining the circular motion.
4.1 Formula for Centripetal Acceleration
The magnitude of centripetal acceleration ((a_c)) is given by the formula:
[
a_c = frac{v^2}{r}
]
Where:
- (v) is the speed of the object.
- (r) is the radius of the circular path.
4.2 Direction of Centripetal Acceleration
The direction of centripetal acceleration is always towards the center of the circle. This constant change in direction is what keeps the object moving along the circular path instead of flying off in a straight line.
5. Non-Uniform Circular Motion
In contrast to uniform circular motion, non-uniform circular motion involves changes in both speed and direction. In this case, tangential acceleration is present and not equal to zero.
5.1 Characteristics of Non-Uniform Circular Motion
- Changing Speed: The object’s speed varies as it moves along the circular path.
- Tangential Acceleration: Acceleration component responsible for the change in speed.
- Centripetal Acceleration: Acceleration component responsible for the change in direction.
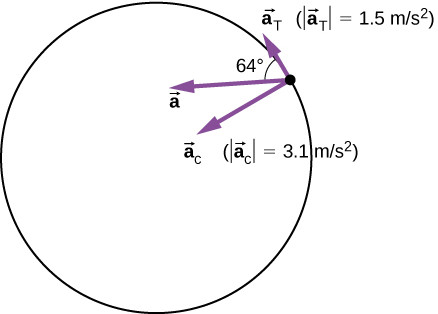
5.2 Total Acceleration in Non-Uniform Circular Motion
The total acceleration in non-uniform circular motion is the vector sum of both tangential and centripetal accelerations.
[
vec{a} = vec{a_t} + vec{a_c}
]
Where:
- (vec{a}) is the total acceleration.
- (vec{a_t}) is the tangential acceleration.
- (vec{a_c}) is the centripetal acceleration.
6. Real-World Examples
Understanding circular motion and tangential acceleration is crucial in various fields of physics and engineering. Here are some examples:
6.1 Uniform Circular Motion Examples
- Satellite Orbiting Earth: A satellite moving at a constant speed in a circular orbit around the Earth experiences uniform circular motion.
- A Car on a Circular Track: When a car moves around a circular track at a constant speed, it exhibits uniform circular motion.
- Merry-Go-Round: Riders on a merry-go-round moving at a constant rate are experiencing uniform circular motion.
6.2 Non-Uniform Circular Motion Examples
- Roller Coaster: A roller coaster moving through a loop increases and decreases speed, demonstrating non-uniform circular motion.
- A Car Speeding Up on a Circular Exit Ramp: A car accelerating around a circular exit ramp showcases non-uniform circular motion.
- Spinning Fan: A fan that speeds up or slows down exhibits non-uniform circular motion.
7. Common Misconceptions
Several misconceptions exist regarding circular motion and tangential acceleration. Let’s address some of them:
7.1 Misconception: Constant Speed Means No Acceleration
- Clarification: Constant speed only means no tangential acceleration. Centripetal acceleration is still present to change the direction of velocity.
7.2 Misconception: Tangential Acceleration is Always Constant
- Clarification: Tangential acceleration is only constant when the rate of change of speed is constant. In many cases, tangential acceleration can vary.
7.3 Misconception: Centripetal Acceleration Changes the Speed
- Clarification: Centripetal acceleration only changes the direction of the velocity, not the speed. Tangential acceleration is responsible for changing the speed.
8. Mathematical Relationships
To fully grasp circular motion, it’s essential to understand the mathematical relationships that govern it.
8.1 Angular Velocity and Angular Acceleration
-
Angular Velocity ((omega)): The rate at which an object rotates or revolves relative to another point.
[
omega = frac{dtheta}{dt}
]Where (dtheta) is the change in angular position and (dt) is the change in time.
-
Angular Acceleration ((alpha)): The rate of change of angular velocity.
[
alpha = frac{domega}{dt}
]
8.2 Relationship between Linear and Angular Quantities
- Linear Speed ((v)):
[
v = romega
] - Tangential Acceleration ((a_t)):
[
a_t = ralpha
]
9. Practical Applications in Engineering and Design
Circular motion principles are fundamental in numerous engineering and design applications.
9.1 Mechanical Engineering
- Rotating Machinery: Understanding centripetal and tangential acceleration is crucial for designing rotating components like turbines, motors, and gears.
- Vehicle Dynamics: Analyzing circular motion helps in designing safer and more efficient vehicles, especially in cornering and handling.
9.2 Aerospace Engineering
- Satellite Orbits: Calculating orbital speeds and accelerations is vital for placing satellites in precise orbits around the Earth.
- Aircraft Maneuvers: Pilots need to understand circular motion to execute turns and loops safely.
9.3 Civil Engineering
- Road Design: Designing curves and bends on roads requires careful consideration of centripetal acceleration to ensure vehicle stability.
- Bridge Design: Understanding rotational forces can aid in designing bridges that withstand environmental stressors.
10. Advanced Concepts
For those looking to delve deeper, let’s explore some advanced concepts related to circular motion.
10.1 Coriolis Effect
The Coriolis effect is an apparent deflection of moving objects when viewed from a rotating reference frame. It significantly affects large-scale phenomena like weather patterns and ocean currents.
10.2 Fictitious Forces
Fictitious forces, also known as pseudo forces, are forces that appear to act on objects in non-inertial (accelerating) reference frames. Examples include the centrifugal force and the Coriolis force.
10.3 Rotational Kinetic Energy
The kinetic energy due to the rotation of an object is known as rotational kinetic energy. It depends on the object’s moment of inertia and angular velocity.
[
KE_{rot} = frac{1}{2}Iomega^2
]
Where:
- (I) is the moment of inertia.
- (omega) is the angular velocity.
11. Uniforms and Their Role in Industries
While discussing the intricacies of physics, it’s important to note how seemingly unrelated fields intersect. At onlineuniforms.net, we supply a variety of uniforms that play a critical role in various industries.
11.1 Safety and Identification
Uniforms often include high-visibility materials and reflective strips, crucial for safety in construction, transportation, and emergency services.
11.2 Professionalism and Branding
Uniforms enhance a company’s image by projecting professionalism and creating a cohesive brand identity. Industries like hospitality, healthcare, and retail rely on uniforms to convey trust and competence.
11.3 Functionality and Comfort
Modern uniforms are designed to offer functionality and comfort, using materials that are durable, breathable, and easy to maintain. This is particularly important in sectors like healthcare, where professionals need to move freely and stay comfortable throughout long shifts.
12. How onlineuniforms.net Can Help
At onlineuniforms.net, we provide high-quality uniforms for various industries, ensuring your team looks professional and feels comfortable. Whether you need medical scrubs, corporate attire, or safety gear, we have you covered.
12.1 Wide Range of Uniforms
We offer a comprehensive selection of uniforms for industries including:
- Healthcare
- Education
- Hospitality
- Corporate
- Security
12.2 Customization Options
Personalize your uniforms with logos, names, and specific designs to enhance your brand identity.
12.3 Quality and Durability
Our uniforms are made from high-quality materials to ensure durability and long-lasting performance.
12.4 Convenient Online Ordering
Easily browse our catalog, customize your selections, and place your order online for a hassle-free experience.
13. Addressing Customer Challenges
We understand the challenges businesses face when sourcing uniforms. Here’s how onlineuniforms.net addresses these issues:
13.1 Finding a Reliable Supplier
We are a trusted provider with a proven track record of delivering high-quality uniforms on time.
13.2 Selecting the Right Uniforms
Our expert team can help you choose the best uniforms for your specific needs, considering factors like industry standards, comfort, and branding.
13.3 Ensuring Proper Fit
We offer detailed sizing guides and assistance to ensure your team gets the perfect fit.
13.4 Customization Needs
Our customization services allow you to create unique uniforms that reflect your brand identity.
14. The onlineuniforms.net Advantage
Choosing onlineuniforms.net means benefiting from:
- Extensive Selection: A wide variety of uniform options to meet diverse needs.
- Superior Quality: Durable, comfortable, and professional-looking uniforms.
- Customization Services: Tailor-made solutions to enhance your brand.
- Excellent Customer Support: Dedicated assistance to ensure a smooth ordering process.
15. Conclusion: Tangential Acceleration and Uniform Circular Motion
In conclusion, tangential acceleration is not constant in uniform circular motion; it is zero. This is because uniform circular motion is defined by constant speed, and tangential acceleration measures the rate of change of speed. Understanding this concept is crucial for grasping the fundamental principles of physics and their applications in various fields. At onlineuniforms.net, we provide the uniforms that professionals rely on, combining quality, functionality, and style to support their important work.
16. Call to Action
Ready to elevate your team’s professional image with high-quality, customized uniforms? Visit onlineuniforms.net today to explore our extensive collection, request a quote, and discover how we can meet your uniform needs. Contact us at +1 (214) 651-8600 or visit our location at 1515 Commerce St, Dallas, TX 75201, United States.
17. FAQs
17.1 What is the primary difference between uniform and non-uniform circular motion?
The primary difference is that uniform circular motion involves constant speed, whereas non-uniform circular motion involves changing speed.
17.2 Can an object moving in a circle have zero acceleration?
No, an object moving in a circle always has centripetal acceleration directed towards the center of the circle.
17.3 What causes tangential acceleration?
Tangential acceleration is caused by a force acting tangentially to the circular path, resulting in a change in speed.
17.4 How is centripetal acceleration calculated?
Centripetal acceleration is calculated using the formula (a_c = frac{v^2}{r}), where (v) is the speed and (r) is the radius of the circular path.
17.5 What is the direction of tangential acceleration?
The direction of tangential acceleration is tangent to the circle, either in the direction of motion (to increase speed) or opposite to it (to decrease speed).
17.6 Is angular velocity constant in uniform circular motion?
Yes, angular velocity is constant in uniform circular motion, as the object covers the same angle in the same amount of time.
17.7 What is the relationship between tangential and angular acceleration?
The relationship is (a_t = ralpha), where (a_t) is tangential acceleration, (r) is the radius, and (alpha) is angular acceleration.
17.8 How do real-world examples illustrate uniform circular motion?
Examples include a satellite orbiting Earth at a constant speed, a car moving on a circular track at constant speed, and riders on a merry-go-round moving at a constant rate.
17.9 What are some common misconceptions about circular motion?
Common misconceptions include believing that constant speed means no acceleration and that centripetal acceleration changes the speed.
17.10 How can onlineuniforms.net assist businesses in finding the right uniforms?
onlineuniforms.net offers a wide range of uniforms, customization options, quality materials, and expert assistance to ensure businesses find the perfect uniforms for their needs.
18. Understanding the Role of Centripetal Force
Centripetal force is crucial in understanding uniform circular motion. It’s the force that makes an object move along a circular path. Without it, the object would continue in a straight line due to inertia.
18.1 What Provides the Centripetal Force?
The centripetal force isn’t a distinct force itself; rather, it’s the role played by another force. Depending on the situation, this force can be:
- Gravity: For satellites orbiting a planet.
- Tension: For an object swung in a circle by a string.
- Friction: For a car turning a corner on a road.
- Electrostatic Force: For electrons orbiting the nucleus in an atom.
18.2 Formula for Centripetal Force
The magnitude of the centripetal force ((F_c)) can be calculated using the formula:
[
F_c = frac{mv^2}{r}
]
Where:
- (m) is the mass of the object.
- (v) is the speed of the object.
- (r) is the radius of the circular path.
19. The Impact of Uniform Circular Motion on Uniform Design
Understanding the principles of physics, like uniform circular motion, can indirectly influence various aspects of design, including uniform design. Uniform design focuses on functionality, safety, and aesthetics.
19.1 Safety Considerations
- High-Visibility Materials: For workers in environments where circular motion is present (e.g., airport ground crews, construction sites near rotating machinery), uniforms with high-visibility materials are essential. These materials reflect light, making workers more visible and reducing the risk of accidents involving moving equipment.
- Durable Fabrics: In industries where workers interact with machinery or vehicles, uniforms made from durable, tear-resistant fabrics are crucial. These fabrics protect against abrasions and impacts, enhancing safety.
19.2 Functionality and Comfort
- Ergonomic Design: Uniforms designed with ergonomics in mind allow for a full range of motion, which is especially important for workers who need to move quickly and efficiently around circular paths.
- Breathable Materials: Workers in hot or strenuous environments benefit from uniforms made from breathable materials that wick away moisture, keeping them cool and comfortable.
19.3 Professionalism and Branding
- Consistent Appearance: Uniforms create a consistent and professional appearance, reinforcing the company’s brand identity.
- Customization: Adding company logos and colors to uniforms enhances brand recognition and fosters a sense of unity among employees.
20. Navigating the Challenges of Uniform Selection and Customization
Selecting and customizing uniforms can be a complex process. Here’s how onlineuniforms.net can help businesses navigate these challenges:
20.1 Understanding Industry-Specific Requirements
Different industries have unique uniform requirements. onlineuniforms.net provides expert guidance to help businesses choose uniforms that meet specific industry standards and regulations.
20.2 Balancing Cost and Quality
onlineuniforms.net offers a range of uniform options to fit different budgets without compromising on quality. Our team can help businesses find the best value for their investment.
20.3 Ensuring Accurate Sizing
Accurate sizing is crucial for comfort and professionalism. onlineuniforms.net provides detailed sizing charts and offers assistance with measuring to ensure a proper fit for all employees.
20.4 Managing Customization Requests
Customizing uniforms can be time-consuming. onlineuniforms.net streamlines the customization process with user-friendly tools and dedicated support, making it easy for businesses to add logos, names, and other branding elements.
21. Testimonials and Success Stories
Hear from businesses that have partnered with onlineuniforms.net to elevate their team’s professional image:
21.1 Healthcare Provider
“onlineuniforms.net provided us with high-quality scrubs that are comfortable, durable, and easy to maintain. Our staff loves them, and they project a professional image to our patients.”
21.2 Construction Company
“The high-visibility vests and durable workwear from onlineuniforms.net have significantly improved safety on our construction sites. The customization options allowed us to reinforce our brand identity.”
21.3 Hospitality Group
“Our team looks sharp and professional in the uniforms from onlineuniforms.net. The quality is excellent, and the customization options allowed us to create a unique look that represents our brand perfectly.”
22. The Future of Uniforms: Innovations and Trends
The uniform industry is constantly evolving. Here are some emerging trends and innovations to watch:
22.1 Smart Uniforms
Smart uniforms incorporate technology such as sensors and wearable devices to monitor worker health, safety, and performance.
22.2 Sustainable Materials
Increasingly, uniforms are being made from sustainable materials such as recycled polyester and organic cotton to reduce environmental impact.
22.3 Enhanced Functionality
Uniforms are being designed with advanced features such as built-in cooling systems, UV protection, and antimicrobial properties to enhance comfort and performance.
23. Case Studies: Uniforms in Action
23.1 Airport Ground Crew
Airport ground crews work in a dynamic environment with frequent circular motion around aircraft. High-visibility uniforms are essential for safety, and durable materials protect against abrasions and impacts.
23.2 Race Car Mechanics
Race car mechanics need uniforms that are functional, comfortable, and fire-resistant. Ergonomic designs allow for a full range of motion, and customization reinforces team identity.
23.3 Amusement Park Staff
Amusement park staff members wear uniforms that are durable, weather-resistant, and visually appealing. Customization helps create a fun and engaging atmosphere for visitors.
24. Contact onlineuniforms.net for Your Uniform Needs
Ready to transform your team’s image with high-quality, customized uniforms? Contact onlineuniforms.net today to explore our extensive collection and discover how we can meet your specific needs.
Address: 1515 Commerce St, Dallas, TX 75201, United States
Phone: +1 (214) 651-8600
Website: onlineuniforms.net
25. Final Thoughts: Linking Physics to Practical Solutions
Understanding concepts like tangential acceleration in uniform circular motion may seem abstract, but they underpin many practical applications in engineering, design, and even uniform selection. At onlineuniforms.net, we bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and real-world solutions, providing uniforms that enhance safety, professionalism, and functionality.
 Workers wearing customized safety vests in a construction site
Workers wearing customized safety vests in a construction site
Whether you need high-visibility gear for workers in motion-intensive environments or professional attire that reflects your brand identity, onlineuniforms.net is your trusted partner. Contact us today to discover how we can elevate your team’s image and performance.
