Navigating the internet can feel overwhelming, but understanding the basics, like what a URL is, makes it much simpler. A URL, or Uniform Resource Locator, is essentially a web address, a unique identifier that helps you locate resources online, and onlineuniforms.net can help you navigate the world of online uniforms. With our wide selection of apparel and accessories, finding the perfect work uniform has never been easier. Learn how URLs direct you to the right resources, and discover the ease of shopping for work uniforms online.
1. Understanding the Core: What is URL (Uniform Resource Locator)?
A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is a unique web address used to identify and locate resources on the internet. It’s like a street address for a website, telling your browser exactly where to find the information you’re looking for. Think of onlineuniforms.net; its URL guides you directly to our site, where you can explore a wide array of uniform options.
1.1. What is the primary function of a URL?
The primary function of a URL is to provide a standardized way to locate a resource on the internet. It specifies the protocol, domain name, and path to a specific file or page, ensuring that your browser knows exactly where to retrieve the requested information. Essentially, it acts as a roadmap, guiding you to the destination you seek on the web.
1.2. What are the key components of a URL?
URLs are composed of several key components:
- Protocol: Specifies how the resource should be accessed (e.g., HTTP, HTTPS).
- Domain Name: Identifies the server hosting the resource (e.g., onlineuniforms.net).
- Path: Specifies the location of the resource on the server (e.g., /collections/healthcare-uniforms).
- Query Parameters (Optional): Provides additional information to the server (e.g., ?color=blue&size=medium).
- Fragment (Optional): Identifies a specific section within the resource (e.g., #sizing-chart).
1.3. How does a URL work in simple terms?
Imagine a URL as a set of instructions for your web browser. When you type a URL into the address bar or click on a link, your browser follows these instructions to find and display the requested resource. The protocol tells the browser how to communicate with the server, the domain name identifies the server, and the path specifies the exact file or page to retrieve.
1.4. Why is the URL called a “Uniform Resource Locator”?
The term “Uniform Resource Locator” accurately describes the function of a URL. “Uniform” indicates that the structure and syntax of URLs are standardized, ensuring consistency across the internet. “Resource” refers to any piece of information that can be identified and accessed on the web, such as a webpage, image, or document. “Locator” signifies that the URL provides the precise location of the resource, enabling browsers to retrieve it.
1.5. What is the difference between a URL and a domain name?
While often used interchangeably, a URL and a domain name are distinct. A domain name (e.g., onlineuniforms.net) is a human-readable address that identifies a website. A URL (e.g., https://onlineuniforms.net/about-us) is a complete web address that includes the protocol, domain name, and path to a specific resource on the website. The domain name is a part of the URL.
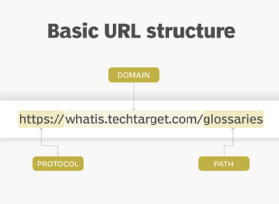
2. Delving Deeper: Anatomy of a URL
Understanding the structure of a URL can help you navigate the web more effectively. Let’s break down the different parts using onlineuniforms.net as an example: https://onlineuniforms.net/collections/chef-uniforms?color=black#sizes.
2.1. What is the protocol or scheme in a URL?
The protocol, or scheme, is the first part of a URL and specifies how your browser should communicate with the server. Common protocols include:
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): The standard protocol for transferring data over the web.
- HTTPS (HTTP Secure): A secure version of HTTP that encrypts data to protect it from eavesdropping.
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol): Used for transferring files between computers.
- Mailto: Used to create email links.
HTTPS is vital for protecting sensitive information, such as passwords and credit card numbers, from unauthorized access. According to a study by Sectigo, 83% of consumers look for the padlock icon in the address bar before submitting personal information on a website.
2.2. What is the host name or domain name in a URL?
The host name, or domain name, is the unique address that identifies a website. It’s the part of the URL that you type into your browser to access a specific site, such as onlineuniforms.net. Domain names are registered with domain name registrars and are associated with IP addresses, which are numerical addresses that computers use to locate each other on the internet.
2.3. What is a subdomain and how is it used?
A subdomain is a prefix added to the main domain name to create a distinct section within a website. For example, blog.onlineuniforms.net could be used to host a blog related to uniforms and workwear. Subdomains are often used to organize different types of content or to create separate websites for different purposes.
2.4. What is the port number in a URL and why is it usually hidden?
The port number specifies the network port that the server uses to listen for incoming connections. For HTTP, the default port is 80, and for HTTPS, it’s 443. Port numbers are usually hidden in URLs because browsers automatically assume the default port based on the protocol. However, if a website uses a non-standard port, it must be explicitly included in the URL (e.g., https://onlineuniforms.net:8080).
2.5. What is the path in a URL and what does it signify?
The path is the part of the URL that follows the domain name and specifies the location of a specific resource on the server. It’s like the directory structure on your computer, guiding the browser to the correct file or page. For example, in the URL https://onlineuniforms.net/collections/chef-uniforms, the path /collections/chef-uniforms indicates that the browser should retrieve the page displaying chef uniforms.
2.6. What are query parameters in a URL and how are they used?
Query parameters are used to pass additional information to the server, often to filter or sort results. They appear after a question mark (?) in the URL and consist of one or more key-value pairs separated by ampersands (&). For example, in the URL https://onlineuniforms.net/search?q=nurse+uniforms&color=blue, the query parameters q=nurse+uniforms and color=blue tell the server to search for nurse uniforms that are blue.
2.7. What is a fragment in a URL and what is its purpose?
A fragment is the part of the URL that follows a hash symbol (#) and identifies a specific section within a webpage. When you click on a link with a fragment, the browser scrolls directly to the corresponding section on the page. For example, in the URL https://onlineuniforms.net/faq#shipping, the fragment #shipping tells the browser to scroll to the section of the FAQ page that answers questions about shipping.
 Basic URL structure diagram with protocol, host name, subdomain, port name, path, query, parameter, and fragment.
Basic URL structure diagram with protocol, host name, subdomain, port name, path, query, parameter, and fragment.
3. The Significance of URL Design
The design of a URL can significantly impact its usability and effectiveness. A well-designed URL is easy to understand, remember, and share, and it can also improve a website’s search engine ranking.
3.1. How can URL design impact user experience?
A clear and descriptive URL can enhance user experience by providing context about the content of the page. Users are more likely to click on a link if the URL gives them a good idea of what to expect. Conversely, a long, complex, or cryptic URL can deter users from clicking, as it may appear suspicious or irrelevant.
3.2. Why are human-readable URLs important?
Human-readable URLs, also known as “speaking URLs,” are URLs that use words that are easy for people to understand. For example, https://onlineuniforms.net/blog/how-to-choose-the-right-uniform is much more human-readable than https://onlineuniforms.net/article?id=1234. Human-readable URLs are easier to remember, share, and type, and they can also improve a website’s search engine ranking.
3.3. How do URLs affect search engine optimization (SEO)?
URLs are a ranking factor in search engine optimization (SEO). Search engines use URLs to understand the content of a page and its relevance to search queries. A well-designed URL that includes relevant keywords can improve a website’s visibility in search results. According to Moz, including keywords in your URL is a best practice for on-page SEO.
3.4. What are some best practices for creating effective URLs?
Here are some best practices for creating effective URLs:
- Use keywords: Include relevant keywords in your URLs to improve SEO.
- Keep it short: Shorter URLs are easier to remember and share.
- Use hyphens: Use hyphens to separate words in your URLs, as this improves readability.
- Avoid underscores: Avoid using underscores in your URLs, as search engines may not recognize them as word separators.
- Use lowercase letters: Use lowercase letters in your URLs, as some servers are case-sensitive.
- Be consistent: Use a consistent URL structure throughout your website.
3.5. How does URL structure contribute to website navigation?
A well-structured URL can make it easier for users to navigate a website. By using a logical and consistent URL structure, you can create a clear hierarchy that reflects the organization of your website’s content. This makes it easier for users to find the information they’re looking for and can improve their overall experience.
4. Security and URLs: HTTP vs. HTTPS
The protocol used in a URL plays a crucial role in the security of your online interactions. HTTP and HTTPS are the two most common protocols, but they offer different levels of protection.
4.1. What is the difference between HTTP and HTTPS?
The main difference between HTTP and HTTPS is that HTTPS encrypts the data transmitted between your browser and the server. This means that sensitive information, such as passwords and credit card numbers, is protected from eavesdropping. HTTP, on the other hand, does not encrypt data, making it vulnerable to interception.
4.2. Why is HTTPS important for online security?
HTTPS is essential for online security because it protects your sensitive information from being stolen. When you visit a website that uses HTTPS, your browser establishes a secure connection with the server, encrypting all data transmitted between them. This prevents hackers from intercepting your data and using it for malicious purposes. A study by Google found that websites using HTTPS have a higher search ranking and lower bounce rate.
4.3. How can you tell if a website is using HTTPS?
You can tell if a website is using HTTPS by looking for the padlock icon in the address bar of your browser. The padlock icon indicates that the connection to the website is secure and that your data is encrypted. Most modern browsers also display the word “Secure” next to the padlock icon.
4.4. What are the risks of using websites that use HTTP?
Using websites that use HTTP poses several risks:
- Data interception: Your data can be intercepted by hackers.
- Man-in-the-middle attacks: Hackers can intercept your communication with the server and modify it without your knowledge.
- Phishing: Hackers can create fake websites that look like legitimate websites to steal your personal information.
- Malware: Hackers can inject malware into websites that use HTTP.
4.5. How does HTTPS protect user data during online transactions?
HTTPS uses a protocol called Transport Layer Security (TLS) to encrypt data during online transactions. TLS creates a secure tunnel between your browser and the server, preventing unauthorized access to your data. This ensures that your credit card numbers, passwords, and other sensitive information remain safe when you make online purchases.
5. URLs and URIs: What’s the Difference?
While the terms URL and URI are often used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings. Understanding the difference between them can help you better grasp the broader concepts of web addressing.
5.1. What is a URI (Uniform Resource Identifier)?
A URI (Uniform Resource Identifier) is a string of characters that identifies a resource on the internet. It’s a more general term than URL and includes both URLs and URNs (Uniform Resource Names).
5.2. How does a URL relate to a URI?
A URL is a specific type of URI that provides information about how to access a resource. In other words, a URL is a URI that includes a protocol and a domain name.
5.3. What is a URN (Uniform Resource Name)?
A URN (Uniform Resource Name) is another type of URI that identifies a resource by name, rather than by location. URNs are designed to be persistent and location-independent, meaning that they can be used to identify a resource even if its location changes.
5.4. Can a URL also be a URI? Explain.
Yes, a URL is a type of URI. A URI is a general term for any string of characters that identifies a resource, while a URL is a specific type of URI that provides information about how to locate that resource on the internet. All URLs are URIs, but not all URIs are URLs.
5.5. Why is it important to understand the difference between URLs and URIs?
Understanding the difference between URLs and URIs can help you better understand the broader concepts of web addressing and resource identification. It can also be helpful when working with web technologies and protocols.
6. URL Shorteners: Making Long URLs Manageable
Long URLs can be cumbersome to share and use. URL shorteners provide a convenient way to create shorter, more manageable URLs that redirect to the original, longer URL.
6.1. What is a URL shortener and how does it work?
A URL shortener is a service that takes a long URL and creates a shorter, more manageable URL that redirects to the original URL. When someone clicks on the shortened URL, they are automatically redirected to the original URL.
6.2. What are the benefits of using URL shorteners?
There are several benefits to using URL shorteners:
- Improved aesthetics: Shorter URLs look cleaner and more professional.
- Easier sharing: Shorter URLs are easier to share on social media and in emails.
- Tracking: Some URL shorteners provide tracking data, such as the number of clicks and the location of users who clicked on the link.
- Masking: URL shorteners can be used to mask the destination URL, which can be useful for affiliate marketing or for hiding sensitive information.
6.3. What are some popular URL shortener services?
Some popular URL shortener services include:
- Bitly
- TinyURL
- Rebrandly
- Short.io
- Bl.ink
6.4. Are there any risks associated with using URL shorteners?
Yes, there are some risks associated with using URL shorteners:
- Security: Shortened URLs can be used to hide malicious websites or phishing scams.
- Link rot: If the URL shortener service shuts down, the shortened URLs will no longer work.
- Privacy: Some URL shorteners track user data, which can raise privacy concerns.
6.5. How can URL shorteners be used effectively in marketing?
URL shorteners can be used effectively in marketing by:
- Tracking campaign performance: Use URL shorteners with tracking features to monitor the performance of your marketing campaigns.
- Creating branded links: Use a URL shortener that allows you to create branded links with your own domain name.
- Improving social media engagement: Use shorter URLs to make your social media posts more visually appealing and easier to share.
7. URL History and Privacy Concerns
Your browsing history, including the URLs you visit, can reveal a lot about your interests and activities. It’s important to be aware of the privacy implications of your URL history and take steps to protect your data.
7.1. How is URL history tracked by browsers and websites?
Browsers track your URL history to provide features like autocomplete and back/forward navigation. Websites can track your URL history through cookies, web analytics tools, and server logs.
7.2. What information is stored in URL history?
URL history typically includes the URLs of the pages you have visited, the date and time of your visits, and the titles of the pages.
7.3. How can URL history be used to compromise user privacy?
URL history can be used to compromise user privacy by:
- Profiling: Your URL history can be used to create a profile of your interests and activities.
- Targeted advertising: Your URL history can be used to target you with personalized ads.
- Identity theft: Your URL history can be used to steal your identity or access your accounts.
- Surveillance: Your URL history can be used for surveillance purposes by governments or law enforcement agencies.
7.4. What steps can users take to protect their URL history?
Users can take several steps to protect their URL history:
- Clear your browsing history regularly: Most browsers allow you to clear your browsing history, cookies, and cache.
- Use private browsing mode: Private browsing mode prevents your browser from storing your browsing history, cookies, and cache.
- Use a VPN: A VPN (Virtual Private Network) encrypts your internet traffic and hides your IP address, making it more difficult to track your URL history.
- Use privacy-focused browsers and search engines: Some browsers and search engines are designed to protect your privacy and do not track your URL history.
7.5. What are the legal and ethical considerations surrounding URL history data retention?
There are several legal and ethical considerations surrounding URL history data retention:
- Data privacy laws: Many countries have data privacy laws that regulate the collection, use, and storage of personal data, including URL history.
- User consent: Websites should obtain user consent before collecting and storing their URL history.
- Data security: Websites should take appropriate measures to protect URL history data from unauthorized access and disclosure.
- Data retention policies: Websites should have clear data retention policies that specify how long URL history data will be stored and how it will be used.
8. Real-World URL Examples
URLs are everywhere online. Let’s look at some real-world examples to illustrate how they are used in different contexts.
8.1. Examples of URLs for e-commerce websites (e.g., onlineuniforms.net)
- Homepage:
https://onlineuniforms.net/ - Category page:
https://onlineuniforms.net/collections/healthcare-uniforms - Product page:
https://onlineuniforms.net/products/womens-scrub-top - Search results page:
https://onlineuniforms.net/search?q=nurse+uniforms - Shopping cart page:
https://onlineuniforms.net/cart - Checkout page:
https://onlineuniforms.net/checkout
8.2. Examples of URLs for news articles and blog posts
- News article:
https://www.nytimes.com/2023/10/26/us/politics/house-speaker-vote.html - Blog post:
https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/what-is-a-url
8.3. Examples of URLs for social media profiles and posts
- Facebook profile:
https://www.facebook.com/zuck - Twitter profile:
https://twitter.com/elonmusk - Instagram post:
https://www.instagram.com/p/CzBI2xVu5K_/
8.4. Examples of URLs for multimedia content (e.g., images, videos, audio)
- Image:
https://www.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/thumbnails/image/web_first_images_release.png - Video:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQw4w9WgXcQ - Audio:
https://www.npr.org/2023/10/26/1208742751/new-order-blue-monday-definitive-story
8.5. How do these examples illustrate the versatility of URLs?
These examples illustrate the versatility of URLs by demonstrating how they are used to identify and locate a wide variety of resources on the internet, including webpages, e-commerce products, news articles, blog posts, social media profiles, and multimedia content. URLs are essential for navigating the internet and accessing the information you need.
9. The Future of URLs
The internet is constantly evolving, and URLs are evolving with it. New technologies and standards are emerging that may change the way we think about and use URLs in the future.
9.1. What are some emerging trends in URL technology?
Some emerging trends in URL technology include:
- Decentralized URLs: Decentralized URLs are based on blockchain technology and are not controlled by a central authority.
- AI-powered URLs: AI-powered URLs can automatically shorten, track, and optimize URLs for marketing purposes.
- Context-aware URLs: Context-aware URLs can adapt to the user’s location, device, and other contextual factors.
9.2. How might URLs change in the future?
URLs may become more intelligent and personalized in the future. They may also become more integrated with other technologies, such as augmented reality and the Internet of Things.
9.3. What role will URLs play in the future of the internet?
URLs will continue to play a vital role in the future of the internet. As the internet becomes more complex and decentralized, URLs will be essential for navigating the vast amount of information and resources available online.
9.4. How will new technologies impact URL structure and function?
New technologies such as blockchain, AI, and context-aware computing may impact URL structure and function by making them more decentralized, intelligent, and personalized.
9.5. What are the potential benefits and challenges of these changes?
The potential benefits of these changes include improved security, privacy, and user experience. The challenges include the need for new standards and protocols, as well as the potential for increased complexity.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About URLs
Here are some frequently asked questions about URLs:
10.1. What is the maximum length of a URL?
The maximum length of a URL is technically unlimited, but most browsers and servers have a limit of around 2,048 characters.
10.2. Are URLs case-sensitive?
URLs are generally case-insensitive, but the path and query parameters may be case-sensitive depending on the server configuration.
10.3. Can URLs contain spaces?
URLs cannot contain spaces. Spaces should be encoded as %20 or replaced with plus signs (+).
10.4. What is URL encoding?
URL encoding is a process of converting characters that are not allowed in URLs into a format that can be transmitted over the internet.
10.5. How do I create a URL for my website?
You can create a URL for your website by registering a domain name and hosting your website on a web server.
10.6. How do I redirect a URL?
You can redirect a URL using a variety of methods, such as using a .htaccess file, a meta refresh tag, or a server-side script.
10.7. What is a canonical URL?
A canonical URL is the preferred URL for a webpage, as specified by the website owner. It is used to prevent duplicate content issues and improve SEO.
10.8. How do I find the URL of an image?
You can find the URL of an image by right-clicking on the image and selecting “Copy Image Address” or “Copy Image URL.”
10.9. What is a relative URL?
A relative URL is a URL that is relative to the current page. It does not include the domain name or protocol.
10.10. How do I use URLs to link to other websites?
You can use URLs to link to other websites by using the <a> tag in HTML.
Ready to find the perfect uniform for your team? Explore our wide selection of high-quality uniforms at onlineuniforms.net.
Contact us today for a quote or visit our store at 1515 Commerce St, Dallas, TX 75201, United States. Call us at +1 (214) 651-8600.

